Visual Studio Code 中的 FastAPI 教程
FastAPI 是一個現代、高效能的 Web 框架,用於使用 Python 構建 API。它旨在輕鬆快速高效地構建 API,同時提供自動驗證、序列化和 API 文件等功能,使其成為構建 Web 服務和微服務的熱門選擇。
在本 FastAPI 教程中,我們將使用 FastAPI 建立一個雜貨清單應用程式。在本教程結束時,您將瞭解如何在 Visual Studio Code 終端、編輯器和偵錯程式中使用 FastAPI。本教程不是 FastAPI 的深入探討。有關詳細資訊,您可以參考 官方 FastAPI 文件。
如果您是第一次使用 Python,我們建議您先學習我們的 Python 教程,以熟悉該語言和 VS Code 的 Python 支援。本教程更適合已經熟悉 Python 並想了解如何在 VS Code 中使用 FastAPI 的使用者。
本 FastAPI 教程的完整程式碼專案可在 GitHub 上找到:python-sample-vscode-fastapi-tutorial。
如果你有任何問題,可以在 Python 擴充套件討論問答中搜索答案或提問。
設定專案
您可以透過多種方式為本教程設定您的專案。我們將介紹如何在 GitHub Codespaces 和 本地 VS Code 中進行設定。
GitHub Codespaces
您可以將此專案設定為在 GitHub Codespaces 中開發,在那裡您可以在 codespace 中遠端編碼、除錯和執行您的應用程式。Codespace 提供了一個完全配置的、託管在雲中的開發環境,無需本地設定。此環境包括專案的依賴項、工具和擴充套件,確保了持續且可復現的開發體驗。它透過提供即時編輯、整合版本控制以及對除錯和測試工具的輕鬆訪問,同時保持專案的安全性和可靠性,從而簡化了協作。
注意:所有 GitHub.com 帳戶在免費版或專業版套餐中都包含每月免費使用 GitHub Codespaces 的配額。有關更多資訊,請訪問 有關 GitHub Codespaces 的計費。
要為此教程設定 codespace,請導航到 此專案的 GitHub 儲存庫。此 codespace 包含快速開始 FastAPI 開發所需的所有必要配置和依賴項。
在本教程中,請選擇 dictionarybased 分支
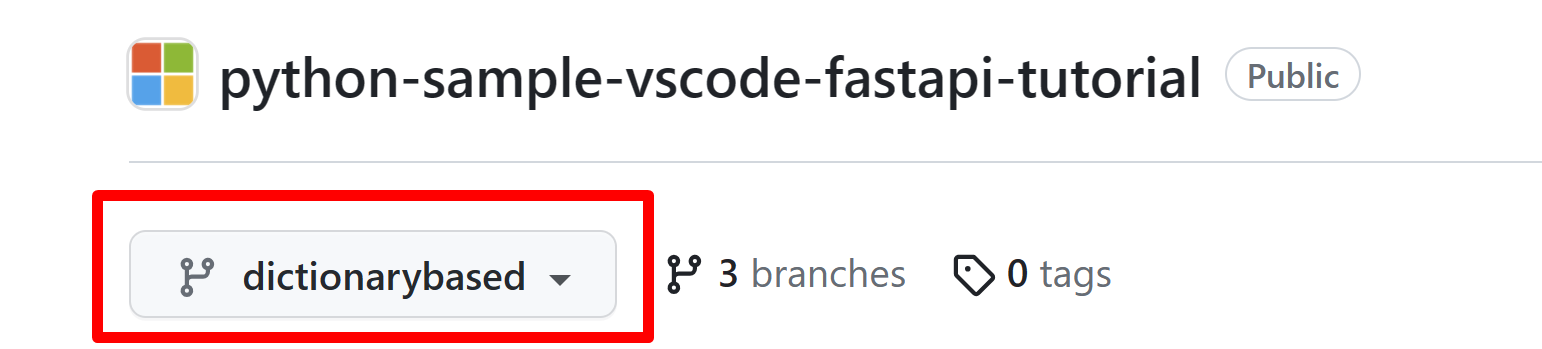
然後,選擇 Code > Codespaces > Create Codespace on <dictionarybased> 分支來建立和開啟專案的 codespace。
完成後,您可以繼續閱讀下面的 替換資料庫 部分。
本地 VS Code 中
要在 VS Code 中成功完成本教程,您首先需要設定 Python 開發環境。具體來說,本教程需要
- Python 3(如果您尚未安裝,請參閱 安裝指南)
- VS Code 的 Python 擴充套件(有關安裝擴充套件的更多詳細資訊,您可以閱讀 擴充套件市場)。
在本節中,我們將建立一個資料夾作為 VS Code 中的工作區開啟,設定一個 Python 虛擬環境,並安裝專案的依賴項。
-
在您的檔案系統中,為本教程建立一個專案資料夾,例如
groceries-plugin。 -
在 VS Code 中開啟此新資料夾(檔案 > 開啟資料夾…)。
-
當出現 工作區信任提示時,選擇 是的,我信任作者 以允許工作區訪問必要的資源和擴充套件。您可以在 文件中瞭解有關工作區信任的更多資訊。
現在,讓我們建立一個 requirements.txt 檔案,其中列出我們要為應用程式安裝的依賴項。requirements.txt 檔案是 Python 開發中的常見做法,用於指定專案依賴的庫及其版本。此檔案有助於確保任何參與專案的人都可以重現相似的開發環境,使其成為維護一致性的便捷元件。
我們將安裝 FastAPI 用於建立應用程式,uvicorn 作為伺服器,以及 Redis 和 type-redis 用於處理資料儲存和與 Redis 資料庫互動。
-
在 VS Code 中建立一個新檔案(檔案 > 新建文字檔案 或 ⌘N(Windows、Linux Ctrl+N))。
-
向其中新增以下內容
fastapi redis types-redis uvicorn -
儲存檔案(⌘S(Windows、Linux Ctrl+S))並將其命名為
requirements.txt。 -
透過開啟命令面板(⇧⌘P(Windows、Linux Ctrl+Shift+P))並執行 Python: Create Environment 命令來建立虛擬環境。
注意:此步驟可能需要幾分鐘才能完成。
-
當被問及環境型別時,請選擇 Venv
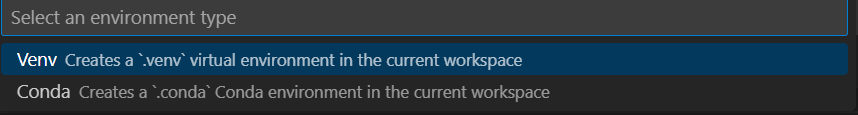
-
然後選擇您計算機上可用的最新版本 Python
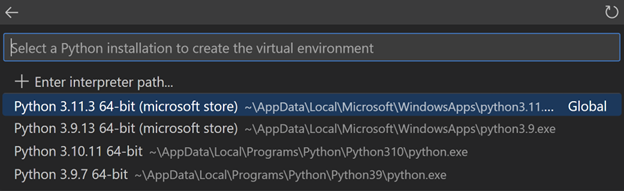
-
從下拉列表中選擇
requirements.txt檔案,以便自動安裝依賴項,然後選擇 OK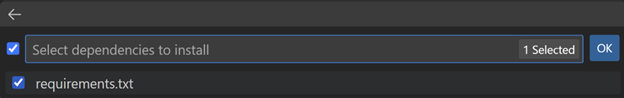
虛擬環境將被建立,依賴項將被自動安裝,並且該環境將被選為您的工作區供 Python 擴充套件使用。您可以透過檢視 VS Code 右下角來確認它已被選中。

注意:如果您在狀態列中找不到新建立的環境資訊,可以單擊 Python 直譯器指示符(或從命令面板執行 Python: Select Interpreter 命令)並手動選擇虛擬環境。
開始編碼
讓我們來建立應用程式!
-
使用 檔案 > 新建檔案… 建立一個新的 Python 檔案,然後選擇 Python 檔案。
-
將其儲存為
main.py(⇧⌘S(Windows、Linux Ctrl+Shift+S)),位於groceries-plugin資料夾中。 -
將以下程式碼新增到
main.py並儲存檔案from fastapi import FastAPI app = FastAPI() @app.get("/") def root(): return {"message": "Hello World"} -
透過啟動偵錯程式(F5)來執行程式碼。
-
從下拉選單中,從列表中選擇 FastAPI 配置選項
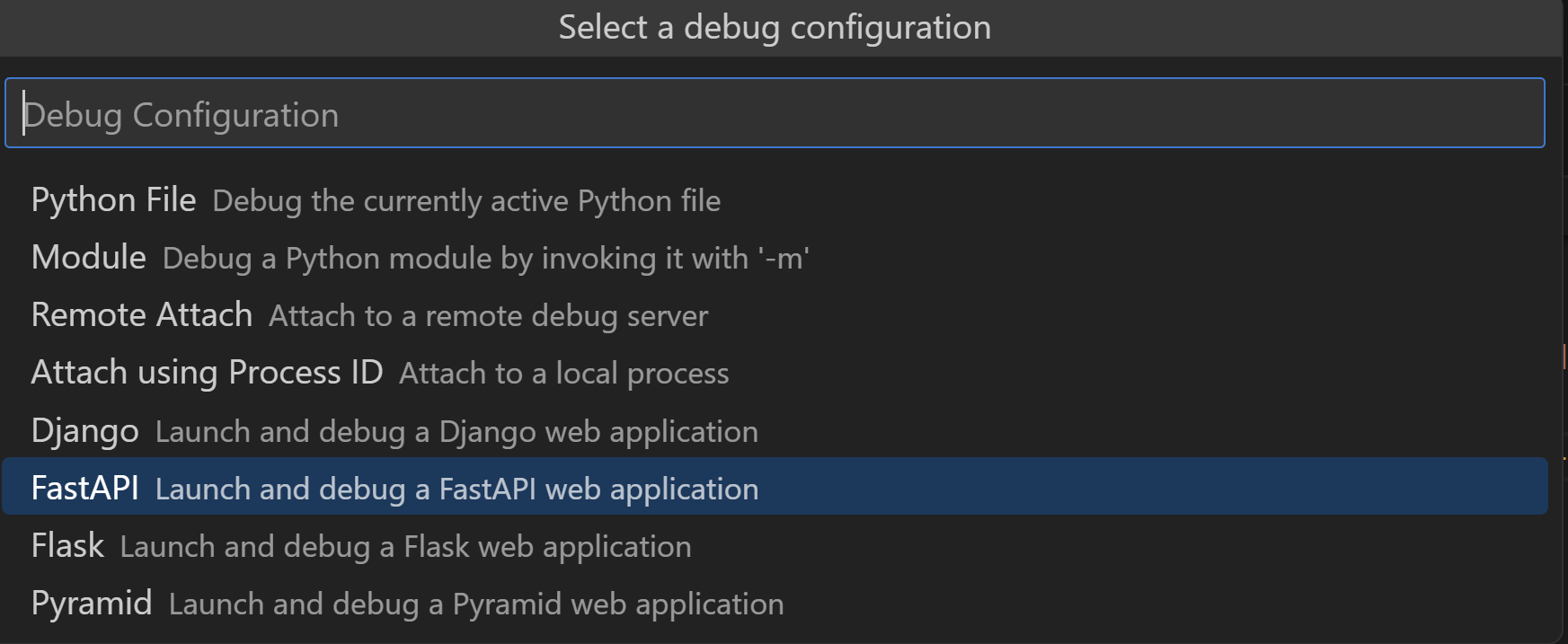
這將自動建立一個除錯配置,透過偵錯程式呼叫 uvicorn 來啟動應用程式伺服器,並允許您逐行程式碼進行檢查,以瞭解其行為。您應該會在終端中看到類似以下內容
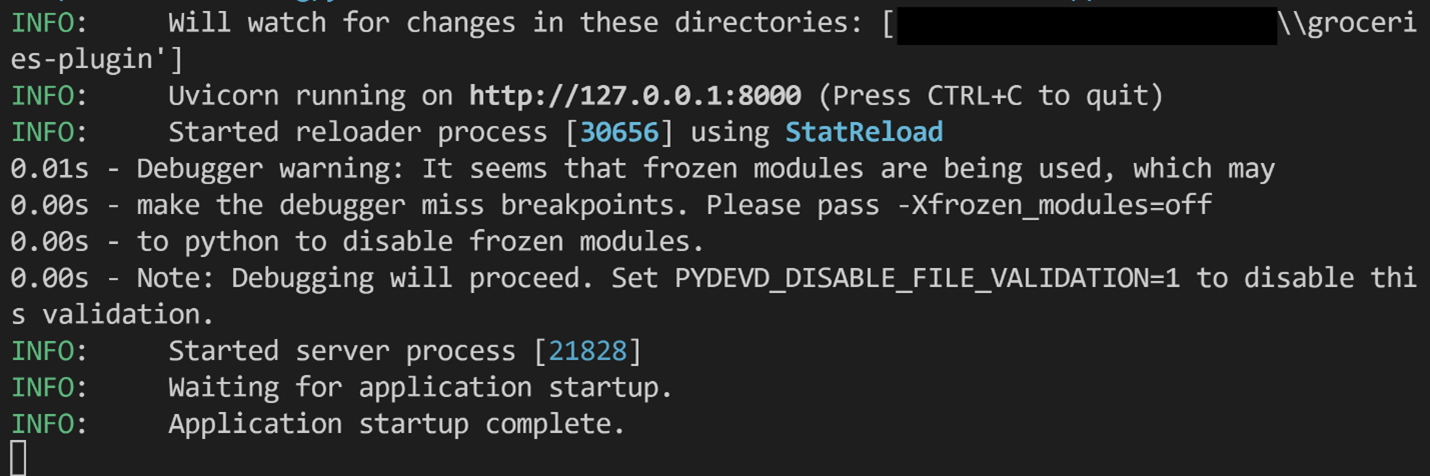
提示:如果您的預設埠已被佔用,請停止偵錯程式,開啟命令面板(⇧⌘P(Windows、Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)),搜尋 Debug: Add Configuration,選擇 Python Debugger,然後選擇 FastAPI。這將建立一個自定義配置檔案
.vscode/launch.json,您可以對其進行編輯。將以下內容新增到"args":[]以設定自定義埠:"--port=5000"。儲存檔案,然後重新啟動偵錯程式(F5)。 -
在終端中按 Ctrl+Click
http://127.0.0.1:8000/URL,以在您的預設瀏覽器中開啟該地址。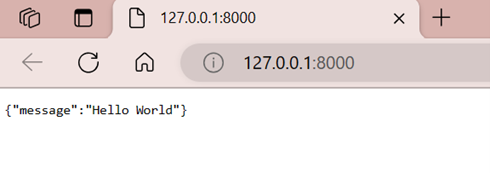
恭喜!您的 FastAPI 應用程式已啟動並執行!
-
透過除錯工具欄上的停止按鈕,或透過 ⇧F5(Windows、Linux Shift+F5)停止偵錯程式。
建立雜貨清單專案的模型
現在我們已經成功運行了 FastAPI 應用程式,我們可以使用 Pydantic 來定義我們的雜貨清單專案。Pydantic 是一個數據驗證和解析庫,可以與 FastAPI 無縫整合。Pydantic 允許您使用具有 型別提示的 Python 類來定義資料模型,以便自動驗證和解析 API 請求中的傳入資料(稱為“payload”).
讓我們為我們的雜貨清單專案建立一個模型。我們將使用 ItemPayload 模型來定義要新增到雜貨清單的專案的資料結構。此模型將包含三個欄位:item_id、item_name 和 quantity。
-
使用 檔案 > 新建檔案… 建立一個新的 Python 檔案,然後選擇 Python 檔案。
-
將以下行新增到檔案中,然後將其儲存在
groceries-plugin資料夾中,命名為models.py(⇧⌘S(Windows、Linux Ctrl+Shift+S))from typing import Optional from pydantic import BaseModel class ItemPayload(BaseModel): item_id: Optional[int] item_name: str quantity: int
Pylance,VS Code 中預設的 Python 語言伺服器,支援型別提示功能,這有助於使用 Pydantic 模型和 FastAPI。這是因為 Pylance 構建在 Pyright 之上,Pyright 是 Python 的靜態型別檢查器,可以檢測程式碼中的型別錯誤,從而防止 bug 並提高程式碼質量。
下面的三個步驟是可選的,但考慮到 FastAPI 廣泛使用型別提示來提高程式碼的可讀性和驗證性,我們可以利用 Pylance 的型別檢查功能來及早捕獲錯誤。
-
開啟設定編輯器(⌘,(Windows、Linux Ctrl+,))。
-
搜尋“python type checking mode”,將其設定為
basic以進行基本型別檢查。Pylance 現在將顯示診斷和警告,以捕獲簡單的型別相關錯誤。或者,您可以將其設定為strict以強制執行更高階的 型別檢查規則。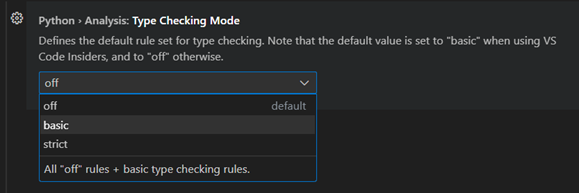
-
接下來,搜尋“Python inlay type hints”,併為變數型別和函式返回型別啟用內嵌提示。

建立路由
現在我們需要一個地方來儲存雜貨清單專案。為簡單起見,讓我們從一個空字典開始。
-
首先,讓我們匯入樣本所需的所有包。開啟
main.py檔案並將第一行匯入替換為以下幾行。from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException from models import ItemPayload -
現在在
app = FastAPI()下方新增以下行。grocery_list: dict[int, ItemPayload] = {}這會建立一個新的空字典,它接收型別為
int(作為專案 ID)的鍵和型別為ItemPayload的值。我們現在將在 FastAPI 應用程式中定義路由。在 Web 應用程式的上下文中,路由就像是將特定 URL 對映到處理它們的程式碼的路徑。這些路由是我們應用程式內不同功能的入口點。當客戶端(如 Web 瀏覽器或其他程式)向我們的應用程式傳送帶有特定 URL 的請求時,FastAPI 會根據 URL 將該請求路由到相應的函式(也稱為路由處理程式或檢視函式),該函式處理請求並生成響應。
讓我們繼續定義用於新增和檢索單個專案以及返回雜貨清單中所有專案的路由。
-
將以下路由新增到
main.py檔案末尾。# Route to add a item @app.post("/items/{item_name}/{quantity}") def add_item(item_name: str, quantity: int): if quantity <= 0: raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="Quantity must be greater than 0.") # if item already exists, we'll just add the quantity. # get all item names items_ids = {item.item_name: item.item_id if item.item_id is not None else 0 for item in grocery_list.values()} if item_name in items_ids.keys(): # get index of item_name in item_ids, which is the item_id item_id = items_ids[item_name] grocery_list[item_id].quantity += quantity # otherwise, create a new item else: # generate an ID for the item based on the highest ID in the grocery_list item_id = max(grocery_list.keys()) + 1 if grocery_list else 0 grocery_list[item_id] = ItemPayload( item_id=item_id, item_name=item_name, quantity=quantity ) return {"item": grocery_list[item_id]}如果您在上部分啟用了型別提示,您可能會注意到 Pylance 會新增函式返回型別的內嵌提示,以及
item_ids和item_id的型別。您可以選擇雙擊每個建議以將其插入程式碼。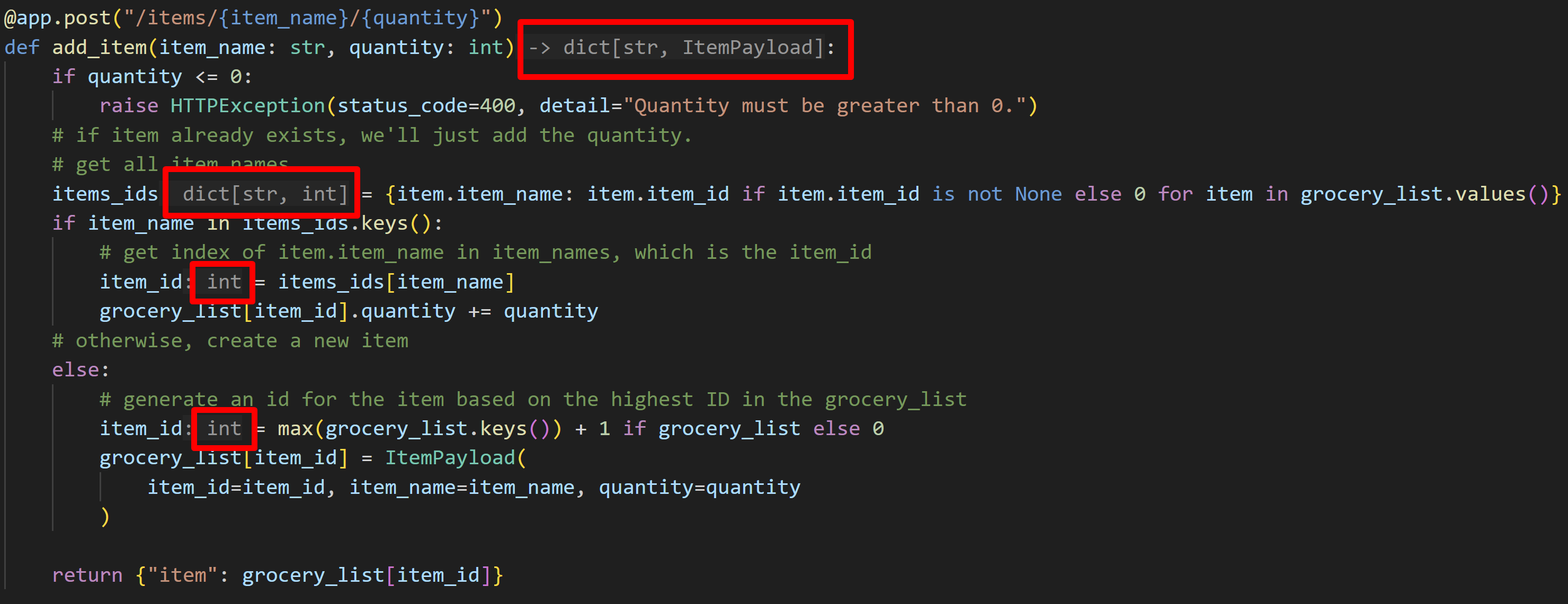
現在讓我們檢查此路由是否按預期工作。最快的方法是同時使用 VS Code 的偵錯程式和 FastAPI 的
/docs端點,它提供了有關所有可用 API 路由的資訊,並允許您與 API 互動以探索其引數和響應。此文件是根據 FastAPI 應用程式中定義的元資料和型別提示動態生成的。 -
在
if quantity <= 0語句旁邊設定一個斷點,方法是單擊行號的左邊距(或 F9)。偵錯程式將在該行執行之前停止,因此您可以逐行檢查程式碼。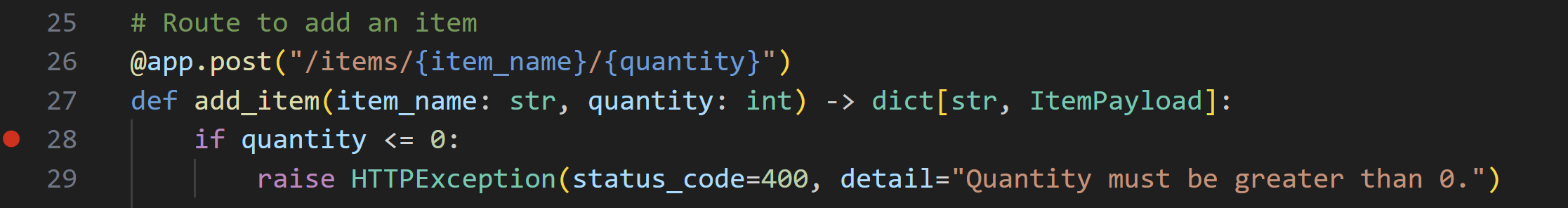
-
啟動偵錯程式(F5),然後到瀏覽器中導航到
http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs。應該會出現一個 Swagger 介面,其中包含應用程式中的兩個端點:
/items和根 (/)。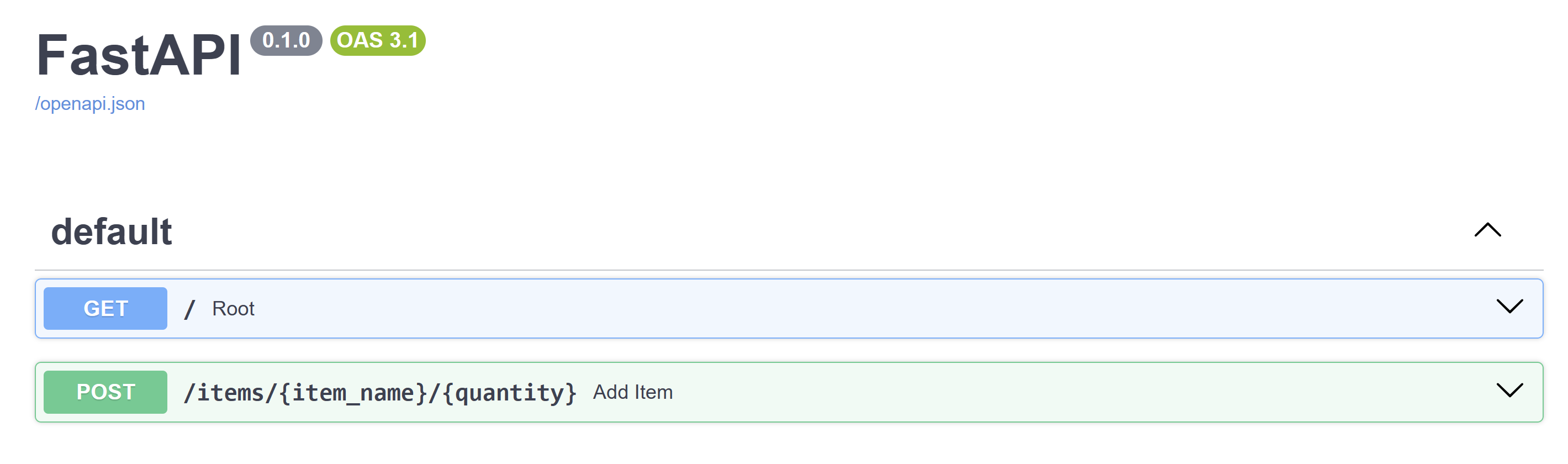
-
選擇
/items路由旁邊的向下箭頭以展開它,然後選擇右側出現的Try it out按鈕。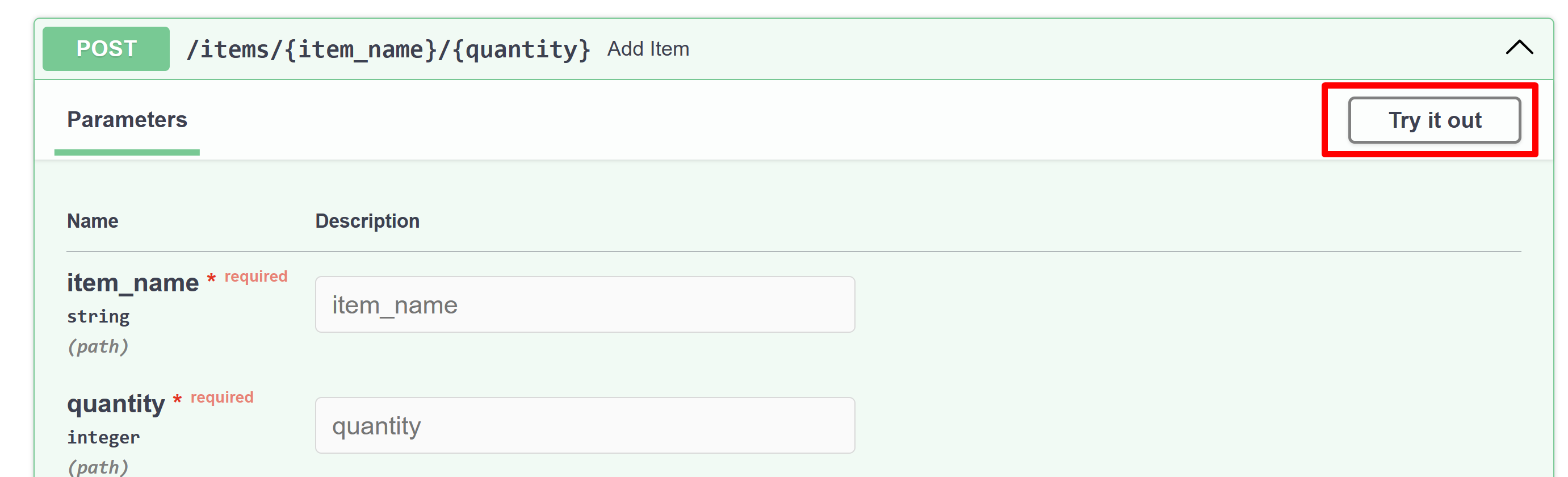
-
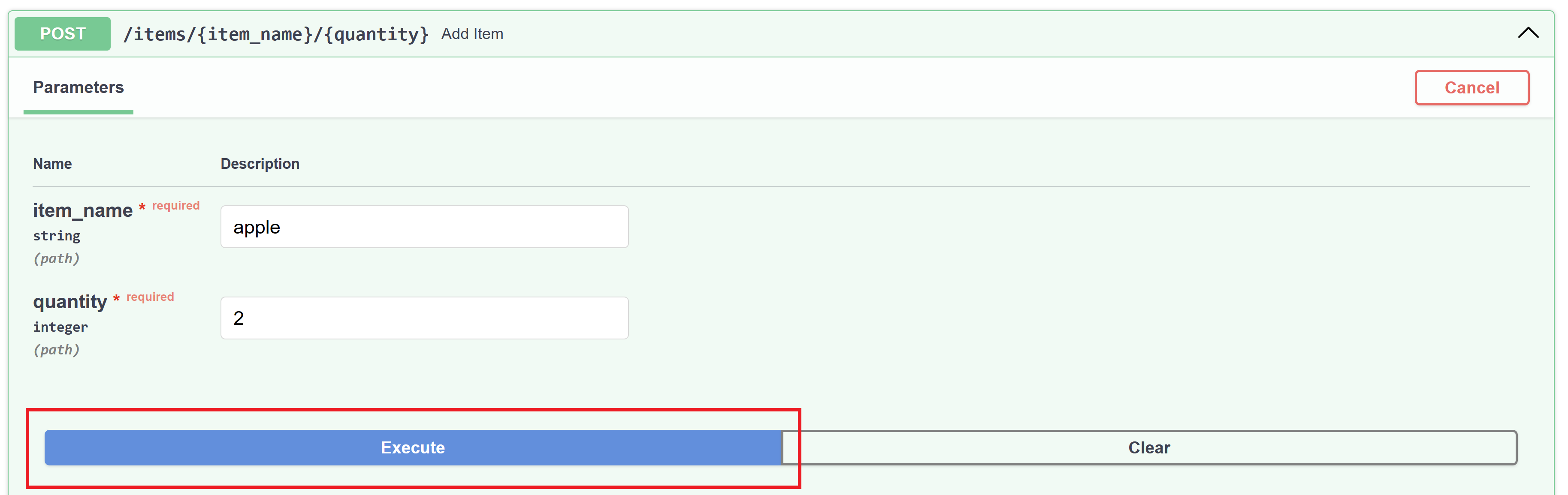
透過向
item_name欄位傳遞一個字串,向quantity欄位傳遞一個數字來新增一個雜貨清單專案。例如,您可以提供“apple”作為item_name,提供 2 作為quantity。 -
選擇 Execute。
-
再次開啟 VS Code,並注意偵錯程式已在您之前設定的斷點處停止。
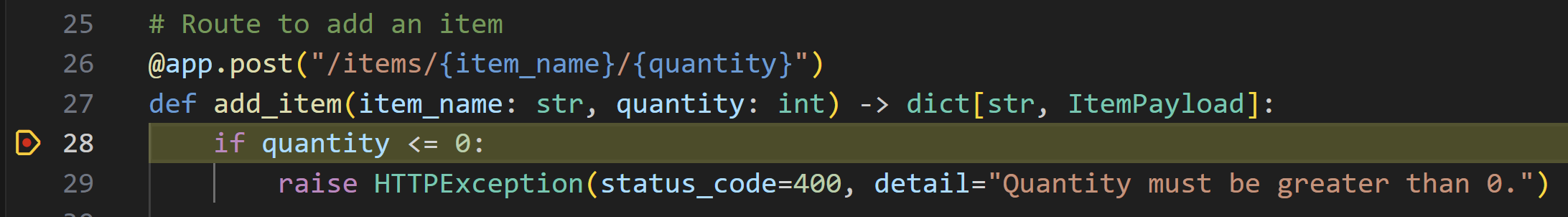
在左側,此時定義的所有區域性和全域性變數都顯示在執行和除錯檢視下的變數視窗中。在我們的示例中,
item_name被設定為 'apple',quantity被設定為 2(在 locals 變數檢視下),並且grocery_list字典為空(在 globals 變數檢視下)。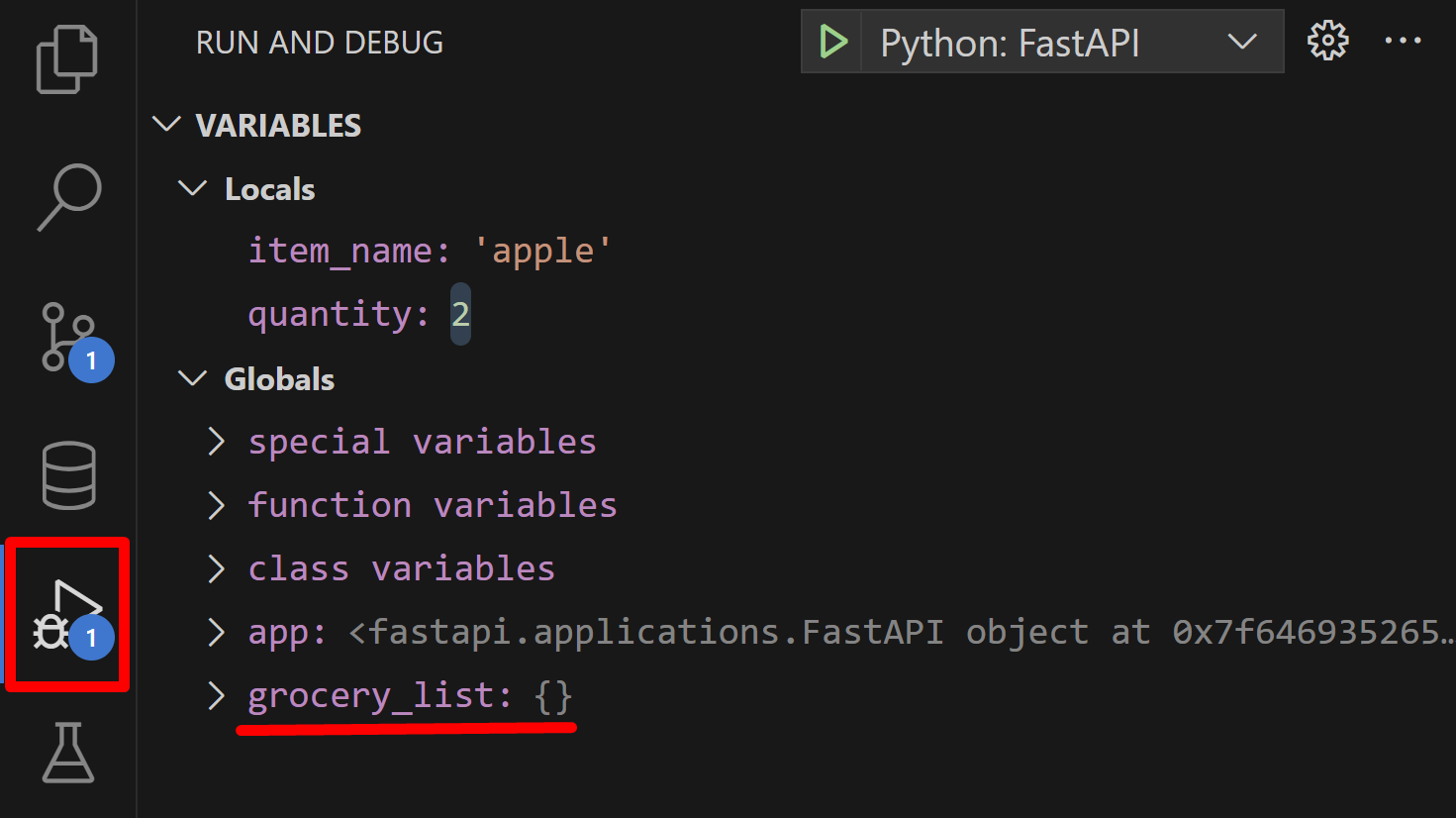
現在讓我們使用 VS Code 的除錯控制檯進行一些探索。
-
選擇
quantity <= 0語句,右鍵單擊編輯器並選擇 Evaluate in Debug Console。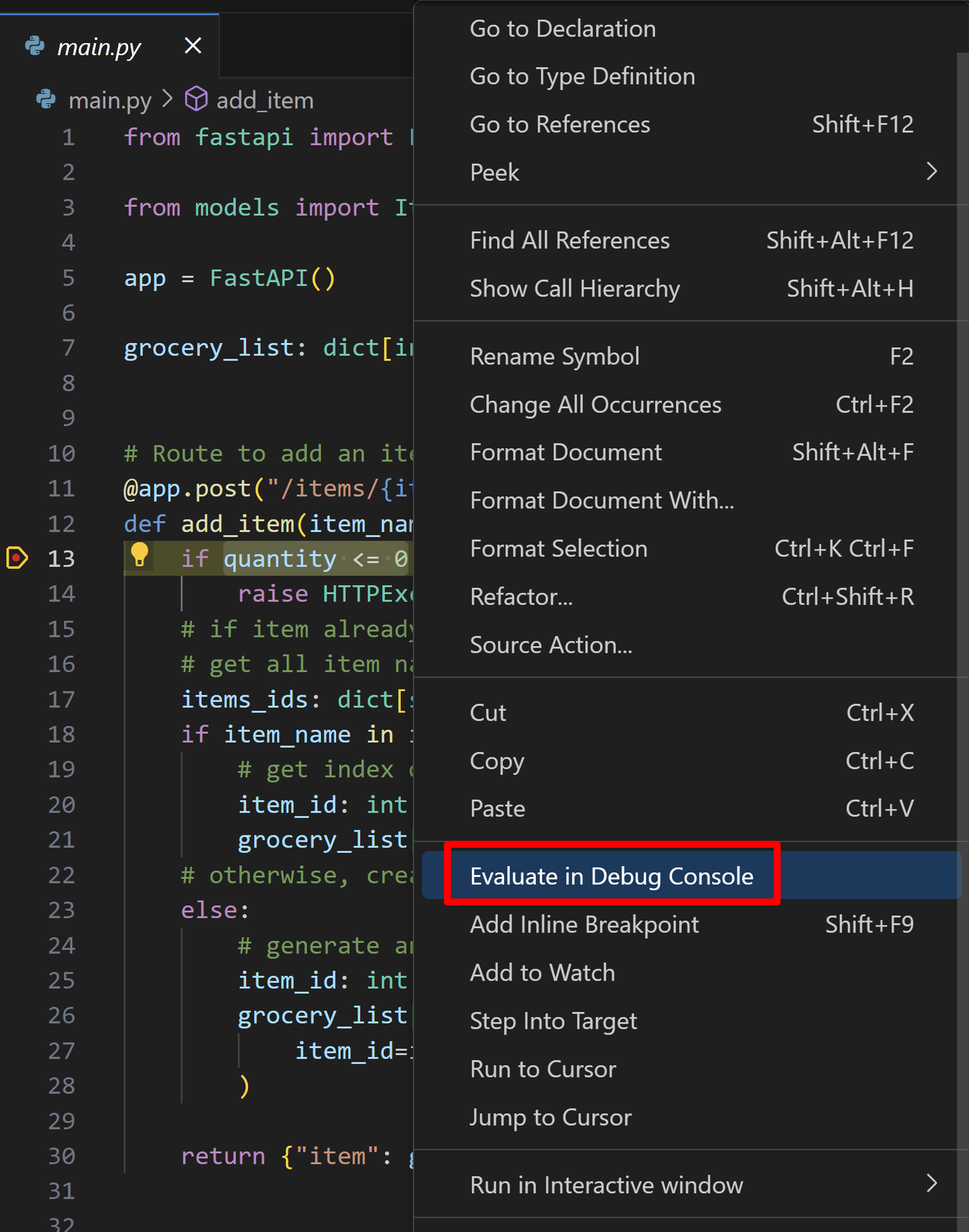
這將開啟除錯控制檯並執行選定的表示式。正如我們在示例中預期的那樣,表示式評估為
False。除錯控制檯可以是一個強大的工具,可以快速測試表達式並更好地理解程式碼在斷點處的狀態。您還可以使用它來執行任意程式碼,例如呼叫函式或列印變數。您可以在 Python 教程中瞭解有關 VS Code 中 Python 除錯的更多資訊。
您現在可以透過在除錯檢視工具欄中選擇 Continue,或者按 F5 來繼續執行程式碼。
最後,讓我們為應用程式新增剩餘的路由,以便我們可以列出所有專案或特定專案,以及從我們的雜貨清單中刪除它們。您可以讓偵錯程式保持執行,因為它會在您儲存下一步所做的更改時自動重新載入應用程式。
-
將
main.py中的內容替換為下面的程式碼。from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException from models import ItemPayload app = FastAPI() grocery_list: dict[int, ItemPayload] = {} # Route to add an item @app.post("/items/{item_name}/{quantity}") def add_item(item_name: str, quantity: int) -> dict[str, ItemPayload]: if quantity <= 0: raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="Quantity must be greater than 0.") # if item already exists, we'll just add the quantity. # get all item names items_ids: dict[str, int] = { item.item_name: item.item_id if item.item_id is not None else 0 for item in grocery_list.values() } if item_name in items_ids.keys(): # get index of item_name in item_ids, which is the item_id item_id: int = items_ids[item_name] grocery_list[item_id].quantity += quantity # otherwise, create a new item else: # generate an ID for the item based on the highest ID in the grocery_list item_id: int = max(grocery_list.keys()) + 1 if grocery_list else 0 grocery_list[item_id] = ItemPayload( item_id=item_id, item_name=item_name, quantity=quantity ) return {"item": grocery_list[item_id]} # Route to list a specific item by ID @app.get("/items/{item_id}") def list_item(item_id: int) -> dict[str, ItemPayload]: if item_id not in grocery_list: raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Item not found.") return {"item": grocery_list[item_id]} # Route to list all items @app.get("/items") def list_items() -> dict[str, dict[int, ItemPayload]]: return {"items": grocery_list} # Route to delete a specific item by ID @app.delete("/items/{item_id}") def delete_item(item_id: int) -> dict[str, str]: if item_id not in grocery_list: raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Item not found.") del grocery_list[item_id] return {"result": "Item deleted."} # Route to remove some quantity of a specific item by ID @app.delete("/items/{item_id}/{quantity}") def remove_quantity(item_id: int, quantity: int) -> dict[str, str]: if item_id not in grocery_list: raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Item not found.") # if quantity to be removed is higher or equal to item's quantity, delete the item if grocery_list[item_id].quantity <= quantity: del grocery_list[item_id] return {"result": "Item deleted."} else: grocery_list[item_id].quantity -= quantity return {"result": f"{quantity} items removed."} -
儲存檔案(⌘S(Windows、Linux Ctrl+S))。應用程式應自動重新載入。
您現在可以再次開啟 /docs 頁面,並測試新路由,使用偵錯程式和除錯控制檯來更好地理解程式碼執行。完成後,您可以停止偵錯程式(⇧F5(Windows、Linux Shift+F5))。您也可以透過單擊來刪除我們在第 4 步中新增的斷點。
恭喜!您現在擁有一個可執行的 FastAPI 應用程式,其中包含用於向雜貨清單新增、列出和刪除專案的路由。
設定資料儲存
此時,您已經擁有了具有基本功能的應用程式的可執行版本。本節將指導您完成資料儲存的設定,以便持久化資料,但如果您對已學到的內容感到滿意,可以選擇跳過它。
到目前為止,我們正在將資料儲存在字典中,這並不理想,因為應用程式重新啟動時所有資料都將丟失。
為了持久化資料,我們將使用 Redis,它是一個開源的記憶體資料結構儲存。由於其速度和多功能性,Redis 通常用作各種應用程式中的資料儲存系統,包括 Web 應用程式、即時分析系統、快取層、本教程等等。
如果您已經在GitHub Codespaces 中使用我們現有的模板進行開發,您可以直接跳到 替換資料庫 部分。
如果您使用的是 Windows,可以透過設定 Docker 容器或 GitHub Codespace 來使用 Redis。在本教程中,我們將使用 Docker 容器,但您可以參考 上面的部分瞭解有關設定 GitHub Codespace 的說明。
否則,如果您使用的是 Linux 或 macOS 計算機,可以透過按照 其網站上的說明來安裝 Redis,然後跳到 替換資料庫部分。
在 Windows 上設定 Docker 容器
VS Code 的 Dev Containers 擴充套件提供了一種簡化的方法,可以將專案、其依賴項以及所有必要的工具整合到一個整潔的容器中,建立一個功能齊全的開發環境。該擴充套件允許您在容器內部(或掛載到容器中)開啟專案,然後在 VS Code 中使用其全部功能。
對於以下步驟,請確保您的計算機上已安裝以下要求:
要求
建立 Dev 容器配置
-
開啟命令面板並執行 Dev Containers: Add Dev Container Configuration Files…。
-
選擇 Python 3
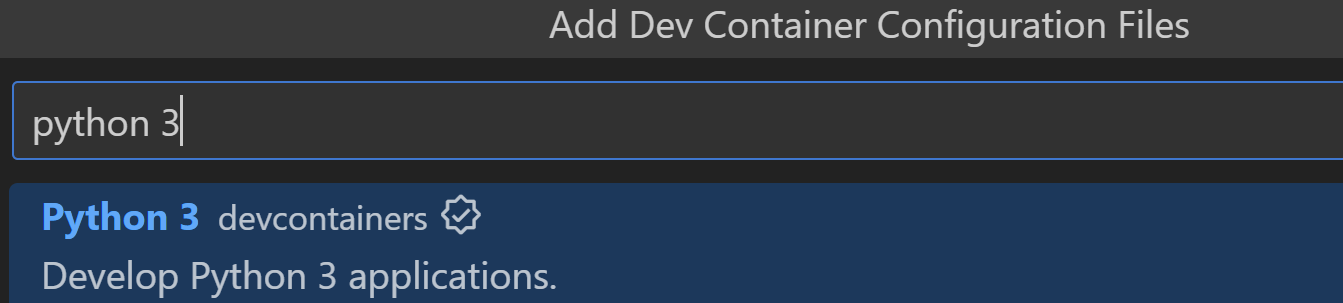
-
選擇預設版本。
-
選擇 Redis Server 作為要安裝的附加功能,按 OK,然後選擇 Keep Defaults。
我們可以選擇安裝 Features 以包含在容器中。在本教程中,我們將安裝 Redis Server,這是一個社群貢獻的功能,它安裝並添加了適用於 Redis 的正確開發容器設定。
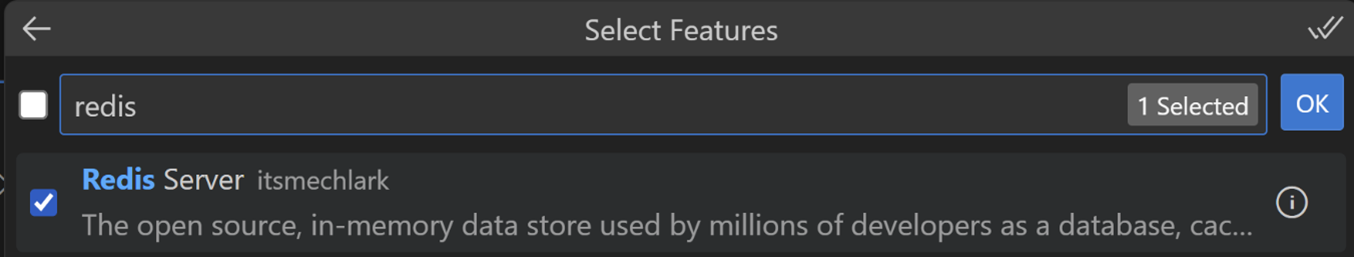
這將會在您的工作區中建立一個
.devcontainer資料夾,其中包含一個devcontainer.json檔案。讓我們對該檔案進行一些編輯,以便容器設定包括安裝我們所需的 VS Code 擴充套件以及專案依賴項等步驟。 -
開啟
devcontainer.json檔案。 -
在
"features" : { ... }條目後面新增一個“,”,以便我們可以向檔案新增更多設定。接下來,我們將在
devcontainer.json檔案中的postCreateCommand屬性中新增必要的依賴項安裝命令,以便在容器設定完成後,我們的應用程式就可以運行了。 -
找到下面的內容並刪除該行上的註釋(
//),以便在容器建立後安裝依賴項。"postCreateCommand": "pip3 install --user -r requirements.txt",您可以在 Development Containers Specification 中瞭解
postCreateCommand和其他生命週期指令碼。現在我們將使用
customizations屬性來新增我們希望安裝在容器中的 VS Code 擴充套件。 -
將以下設定新增到
devcontainer.json。// Use 'postCreateCommand' to run commands after the container is created. "postCreateCommand": "pip3 install --user -r requirements.txt", // Configure tool-specific properties. "customizations": { "vscode": { "extensions": [ "ms-python.python", //Python extension ID "ms-python.vscode-pylance" //Pylance extension ID ] } } -
儲存檔案。
-
在右下角顯示的通知中選擇 Reopen in Container,或者從命令面板執行 Dev Containers: Reopen in Container 命令。
注意:根據網際網路速度和機器效能,構建容器可能需要幾分鐘時間。
您可以在 Dev Containers 文件中瞭解有關開發容器配置的更多資訊。
完成後,您將擁有一個完全配置的基於 Linux 的工作區,其中安裝了 Python 3 和 Redis Server。
容器設定完成後,您會在 VS Code 左下角看到一個指示符。
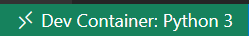
注意:透過開啟擴充套件檢視(⇧⌘X(Windows、Linux Ctrl+Shift+X))並搜尋 Python 和 Pylance 擴充套件,仔細檢查它們是否已成功安裝在容器中。如果沒有,您可以透過執行 Install in Dev Container 來安裝它們。
選定的 Python 直譯器資訊可在右下角的狀態列中找到,與 devcontainer.json 檔案中指定的版本匹配。
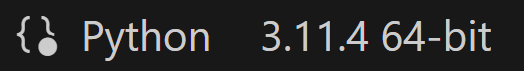
注意:如果您在狀態列中找不到 Python 直譯器資訊,可以單擊 Python 直譯器指示符(或從命令面板執行 Python: Select Interpreter 命令)並手動選擇容器中的 Python 直譯器。
我們現在已準備好進入下一部分,屆時我們將替換資料儲存。
替換資料庫
我們有一個儲存雜貨清單專案的字典,但我們希望用 Redis 資料庫替換它。在本教程中,我們將使用 Redis hash 來儲存我們的資料,Redis hash 是一種可以儲存多個鍵值對的資料結構。
與傳統資料庫不同,您可以在不知道其 ID 的情況下檢索專案,而在這裡,您需要知道 Redis hash 鍵才能從中檢索值。在本教程中,我們將建立一個名為 item_name_to_id 的 hash 來按名稱檢索專案,並將它們對映到它們的 ID。此外,我們將建立其他 hash 來按 ID 檢索專案,並將它們對映到它們的名稱和數量。每個專案 hash 都命名為 item_id:{item_id},並有兩個欄位:item_name 和 quantity。
首先,讓我們開始用連線到 Redis 伺服器的 Redis 客戶端物件替換字典。
-
在
main.py檔案中,將檔案開頭的grocery_list: dict[int, ItemPayload] = {}替換為下面的行。redis_client = redis.StrictRedis(host='0.0.0.0', port=6379, db=0, decode_responses=True)Pylance 會顯示一個錯誤訊息,因為尚未匯入 Redis。
-
將游標放在編輯器中的“redis”上,然後單擊顯示的燈泡圖示(或 ⌘.(Windows、Linux Ctrl+.))。然後選擇 Add 'import redis'。
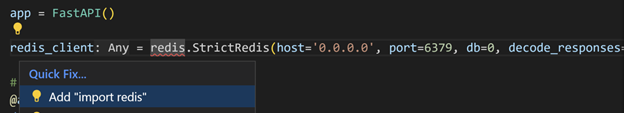
提示:您可以透過在設定編輯器(⌘,(Windows、Linux Ctrl+,))中查詢Auto Import Completions 設定並啟用它,來設定 Pylance 以自動新增匯入。
我們現在有一個 Redis 客戶端物件,它連線到本地主機(
host="0.0.0.0")上執行的 Redis 伺服器,並監聽埠 6379(port=6379)。db引數指定要使用的 Redis 資料庫。Redis 支援多個數據庫,在此程式碼中,我們將使用資料庫 0,這是預設資料庫。我們還傳遞了decode_responses=True,以便響應被解碼為字串(而不是位元組)。讓我們在第一個路由
add_item中進行一些替換。我們不再需要檢視字典中的所有鍵來查詢提供的專案名稱,而是可以直接從 Redis hash 中獲取該資訊。我們假設
item_name_to_idhash 已經存在,將專案名稱對映到它們的 ID(別擔心,我們稍後會新增這段程式碼!)。然後,我們可以透過呼叫 Redis 的hget方法來獲取請求中收到的專案名稱的 ID,如果請求的名稱已存在於 hash 中,則返回專案 ID,否則返回None。 -
刪除帶有以下內容的行。
items_ids = {item.item_name: item.item_id if item.item_id is not None else 0 for item in grocery_list.values()}並替換為
item_id = redis_client.hget("item_name_to_id", item_name)請注意,Pylance 會在此更改中報告一個問題。這是因為
hget方法返回str或None(如果專案不存在)。但是,我們尚未替換的程式碼下面的行期望item_id為int型別。讓我們透過重新命名item_id符號來解決此警告。 -
將
item_id重新命名為item_id_str。 -
如果啟用了內嵌提示,Pylance 應該會在
item_id_str旁邊顯示一個變數型別提示。您可以選擇雙擊以接受它。
-
如果專案不存在,則
item_id_str為None。所以現在我們可以刪除以下內容的行。if item_name in items_ids.keys():並替換為
if item_id_str is not None:現在我們有了專案 ID 的字串形式,我們需要將其轉換為
int並更新專案的數量。目前,我們的 Redis hash 只將專案名稱對映到它們的 ID。為了也將專案 ID 對映到它們的名稱和數量,我們將為每個專案建立一個單獨的 Redis hash,使用"item_id:{item_id}"作為我們的 hash 名稱,以方便按 ID 檢索。我們還將為這些 hash 新增item_name和quantity欄位。 -
刪除
if塊內的程式碼。item_id: int = items_ids[item_name] grocery_list[item_id].quantity += quantity並新增以下內容,將
item_id轉換為int,然後透過呼叫 Redis 的hincrby方法來增加專案的數量。此方法會將其遞增請求(quantity)提供的數量增加"quantity"欄位的值。item_id = int(item_id_str) redis_client.hincrby(f"item_id:{item_id}", "quantity", quantity)現在我們只需要替換專案不存在時(當
item_id_str為None時)的程式碼。在這種情況下,我們生成一個新的item_id,為專案建立一個新的 Redis hash,然後新增提供的專案名稱和數量。為了生成一個新的
item_id,讓我們使用 Redis 的incr方法,傳遞一個名為"item_ids"的新 hash。此 hash 用於儲存最後一個生成的 ID,因此每次建立新專案時都可以對其進行遞增,確保它們都有唯一的 ID。 -
刪除帶有以下內容的行。
item_id: int = max(grocery_list.keys()) + 1 if grocery_list else 0並新增以下內容。
item_id: int = redis_client.incr("item_ids")當
item_ids鍵第一次執行此incr呼叫時,Redis 會建立該鍵並將其對映到值1。然後,每次執行時,它都會將儲存的值增加 1。現在,我們將使用
hset方法將專案新增到 Redis hash 中,並提供欄位(item_id、item_name和quantity)的對映,以及值(專案新生成的 ID 及其提供的名稱和數量)。 -
刪除帶有以下內容的行。
grocery_list[item_id] = ItemPayload( item_id=item_id, item_name=item_name, quantity=quantity )並替換為以下內容。
redis_client.hset( f"item_id:{item_id}", mapping={ "item_id": item_id, "item_name": item_name, "quantity": quantity, })現在我們只需要將新生成的 ID 對映到專案名稱,方法是設定我們在開頭引用的 hash,即
item_name_to_id。 -
將此行新增到路由末尾的
else塊內。redis_client.hset("item_name_to_id", item_name, item_id) -
刪除帶有以下內容的行。
return {"item": grocery_list[item_id]}並替換為
return {"item": ItemPayload(item_id=item_id, item_name=item_name, quantity=quantity)} -
如果您願意,可以嘗試對其他路由進行類似的替換。否則,您可以將檔案的全部內容替換為下面的行。
import redis from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException from models import ItemPayload app = FastAPI() redis_client = redis.StrictRedis(host="0.0.0.0", port=6379, db=0, decode_responses=True) # Route to add an item @app.post("/items/{item_name}/{quantity}") def add_item(item_name: str, quantity: int) -> dict[str, ItemPayload]: if quantity <= 0: raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="Quantity must be greater than 0.") # Check if item already exists item_id_str: str | None = redis_client.hget("item_name_to_id", item_name) if item_id_str is not None: item_id = int(item_id_str) redis_client.hincrby(f"item_id:{item_id}", "quantity", quantity) else: # Generate an ID for the item item_id: int = redis_client.incr("item_ids") redis_client.hset( f"item_id:{item_id}", mapping={ "item_id": item_id, "item_name": item_name, "quantity": quantity, }, ) # Create a set so we can search by name too redis_client.hset("item_name_to_id", item_name, item_id) return { "item": ItemPayload(item_id=item_id, item_name=item_name, quantity=quantity) } # Route to list a specific item by ID but using Redis @app.get("/items/{item_id}") def list_item(item_id: int) -> dict[str, dict[str, str]]: if not redis_client.hexists(f"item_id:{item_id}", "item_id"): raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Item not found.") else: return {"item": redis_client.hgetall(f"item_id:{item_id}")} @app.get("/items") def list_items() -> dict[str, list[ItemPayload]]: items: list[ItemPayload] = [] stored_items: dict[str, str] = redis_client.hgetall("item_name_to_id") for name, id_str in stored_items.items(): item_id: int = int(id_str) item_name_str: str | None = redis_client.hget(f"item_id:{item_id}", "item_name") if item_name_str is not None: item_name: str = item_name_str else: continue # skip this item if it has no name item_quantity_str: str | None = redis_client.hget( f"item_id:{item_id}", "quantity" ) if item_quantity_str is not None: item_quantity: int = int(item_quantity_str) else: item_quantity = 0 items.append( ItemPayload(item_id=item_id, item_name=item_name, quantity=item_quantity) ) return {"items": items} # Route to delete a specific item by ID but using Redis @app.delete("/items/{item_id}") def delete_item(item_id: int) -> dict[str, str]: if not redis_client.hexists(f"item_id:{item_id}", "item_id"): raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Item not found.") else: item_name: str | None = redis_client.hget(f"item_id:{item_id}", "item_name") redis_client.hdel("item_name_to_id", f"{item_name}") redis_client.delete(f"item_id:{item_id}") return {"result": "Item deleted."} # Route to remove some quantity of a specific item by ID but using Redis @app.delete("/items/{item_id}/{quantity}") def remove_quantity(item_id: int, quantity: int) -> dict[str, str]: if not redis_client.hexists(f"item_id:{item_id}", "item_id"): raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Item not found.") item_quantity: str | None = redis_client.hget(f"item_id:{item_id}", "quantity") # if quantity to be removed is higher or equal to item's quantity, delete the item if item_quantity is None: existing_quantity: int = 0 else: existing_quantity: int = int(item_quantity) if existing_quantity <= quantity: item_name: str | None = redis_client.hget(f"item_id:{item_id}", "item_name") redis_client.hdel("item_name_to_id", f"{item_name}") redis_client.delete(f"item_id:{item_id}") return {"result": "Item deleted."} else: redis_client.hincrby(f"item_id:{item_id}", "quantity", -quantity) return {"result": f"{quantity} items removed."} -
重新執行偵錯程式,透過與
/docs路由進行互動來測試此應用程式。完成後,您可以停止偵錯程式。
恭喜!您現在擁有一個可執行的 FastAPI 應用程式,其中包含用於從雜貨清單新增、列出和刪除專案的路由,並且資料已持久化到 Redis 資料庫中。
可選:設定資料庫刪除
現在資料已由 Redis 持久化,您可能希望建立一個指令碼來刪除所有測試資料。要做到這一點,請建立一個名為 flushdb.py 的新檔案,其中包含以下內容。
import redis
redis_client = redis.StrictRedis(host='0.0.0.0', port=6379, db=0, decode_responses=True)
redis_client.flushdb()
然後,當您想重置資料庫時,可以在 VS Code 中開啟 flushdb.py 檔案,然後選擇編輯器右上角的Run按鈕,或者從命令面板執行 Python: Run Python File in Terminal 命令。
請注意,這應該謹慎進行,因為它將刪除當前資料庫中的所有鍵,如果在生產環境中執行,可能會導致資料丟失。
可選:建立 GPT Action
使用 GitHub Codespaces,您可以在使用 GPT Actions 進行測試時託管您的應用程式。GPT Actions 是使 ChatGPT 能夠與現有 API 互動以增強其功能的工具,使其能夠執行廣泛的操作。您可以觀看下面的直播錄影,建立自己的 ChatGPT 雜貨清單外掛。
注意:所有個人 GitHub.com 帳戶在免費版或專業版套餐中都包含每月免費使用 GitHub Codespaces 的配額。有關更多資訊,請訪問 有關 GitHub Codespaces 的計費。
後續步驟
感謝您跟隨本教程!希望您學到了有關 FastAPI 以及如何在 VS Code 中使用它的新知識。
本教程的完整程式碼專案可在 GitHub 上找到:python-sample-vscode-fastapi-tutorial。
在 官方文件中瞭解有關 FastAPI 的更多資訊。
要嘗試在生產網站上執行此應用程式,請檢視教程 使用 Docker 容器將 Python 應用程式部署到 Azure App Service。
您還可以檢視以下其他 VS Code Python 文章。