LoRA 微調 Phi Silica
您可以使用低秩適配(LoRA)來微調 Phi Silica 模型,以提高其在特定用例中的效能。透過使用 LoRA 最佳化 Microsoft Windows 本地語言模型 Phi Silica,您可以獲得更準確的結果。此過程包括訓練 LoRA 介面卡,然後在推理過程中應用它來提高模型的準確性。
Phi Silica 功能在中國不可用。
先決條件
- 您已確定一個用例,用於增強 Phi Silica 的響應。
- 您已選擇一個評估標準來決定什麼是“良好響應”。
- 您已嘗試過 Phi Silica API,但它們不符合您的評估標準。
訓練您的介面卡
要使用 Windows 11 和 LoRA 介面卡微調 Phi Silica 模型,您必須首先生成一個供訓練過程使用的資料集。
生成用於 LoRA 介面卡的資料集
要生成資料集,您需要將資料分成兩個檔案
train.json:用於訓練介面卡。test.json:用於在訓練期間和之後評估介面卡的效能。
兩個檔案都必須使用 JSON 格式,其中每一行是一個單獨的 JSON 物件,代表一個樣本。每個樣本應包含使用者和助手之間交換的訊息列表。
每個訊息物件都需要兩個欄位
content:訊息的文字。role:可以是"user"或"assistant",表示發件人。
請參閱以下示例
{"messages": [{"content": "Hello, how do I reset my password?", "role": "user"}, {"content": "To reset your password, go to the settings page and click 'Reset Password'.", "role": "assistant"}]}
{"messages": [{"content": "Can you help me find nearby restaurants?", "role": "user"}, {"content": "Sure! Here are some restaurants near your location: ...", "role": "assistant"}]}
{"messages": [{"content": "What is the weather like today?", "role": "user"}, {"content": "Today's forecast is sunny with a high of 25°C.", "role": "assistant"}]}
訓練技巧
- 每個樣本行末尾不需要逗號。
- 包含儘可能多高質量且多樣化的示例。為獲得最佳效果,請在您的
train.json檔案中收集至少幾千個訓練樣本。 test.json檔案可以更小,但應涵蓋您期望模型處理的互動型別。- 建立
train.json和test.json檔案,每行包含一個 JSON 物件,其中包含使用者和助手之間簡短的來回對話。資料的質量和數量將極大地影響 LoRA 介面卡的有效性。
訓練 LoRA 介面卡
要訓練 LoRA 介面卡,您需要以下必需的先決條件
- 具有可用配額的 Azure 訂閱,位於 Azure 容器應用中。
- 我們建議使用 A100 GPU 或更高級別的 GPU 來高效執行微調作業。
- 檢查您在 Azure 門戶中是否有可用配額。如果您需要有關查詢配額的幫助,請參閱 檢視配額。
按照以下步驟建立工作區並啟動微調作業
-
導航到 **模型工具 > 微調**,然後選擇 **新建專案**。
-
從模型目錄中選擇 "microsoft/phi-silica",然後選擇 **下一步**。
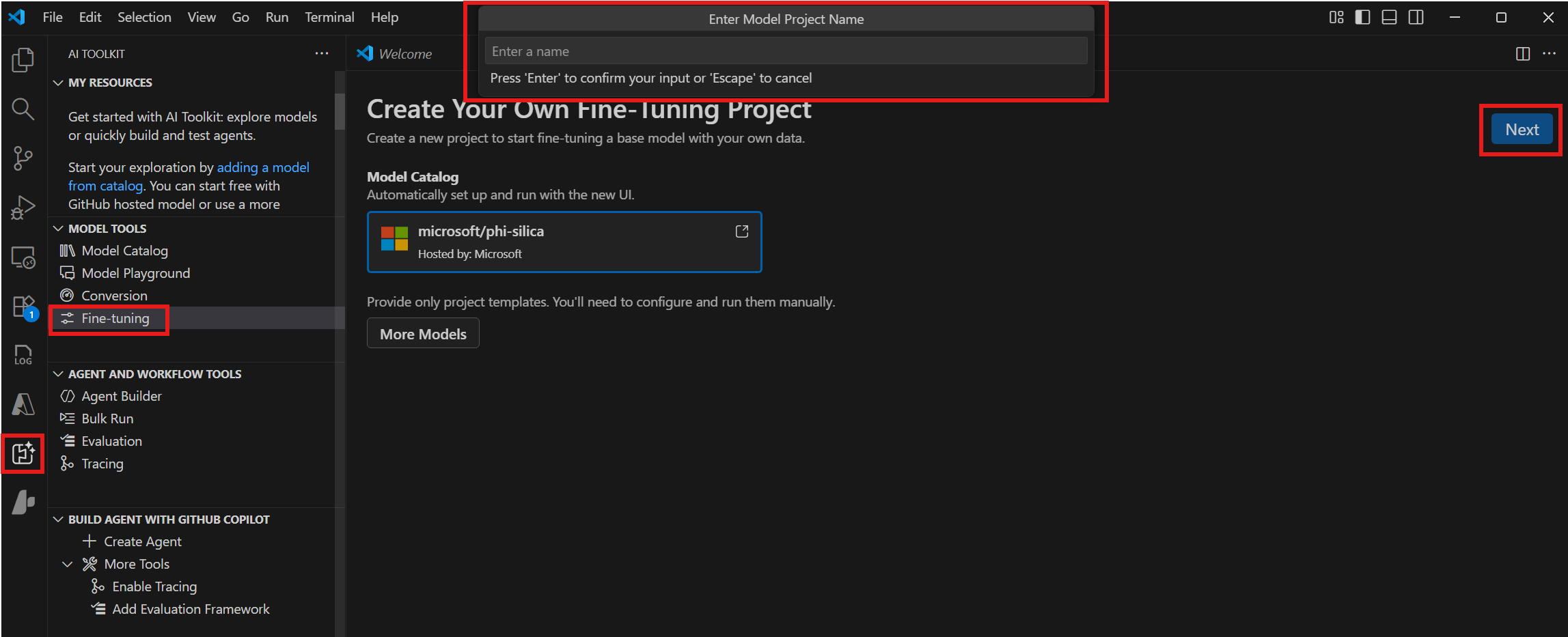
-
在對話方塊中,選擇一個專案資料夾並輸入專案名稱。專案的新 VS Code 視窗將開啟。
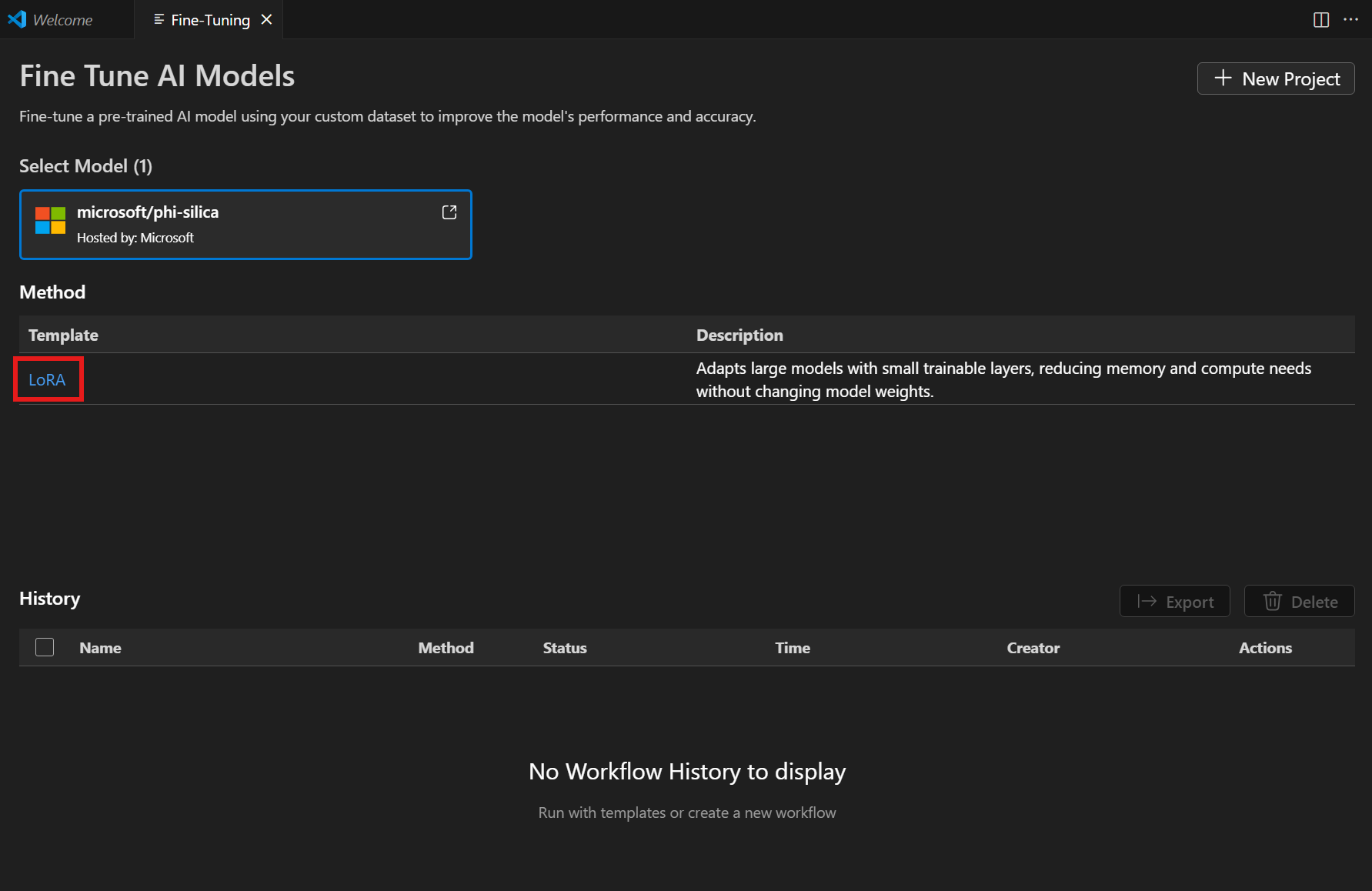
-
從方法列表中選擇 "LoRA"。
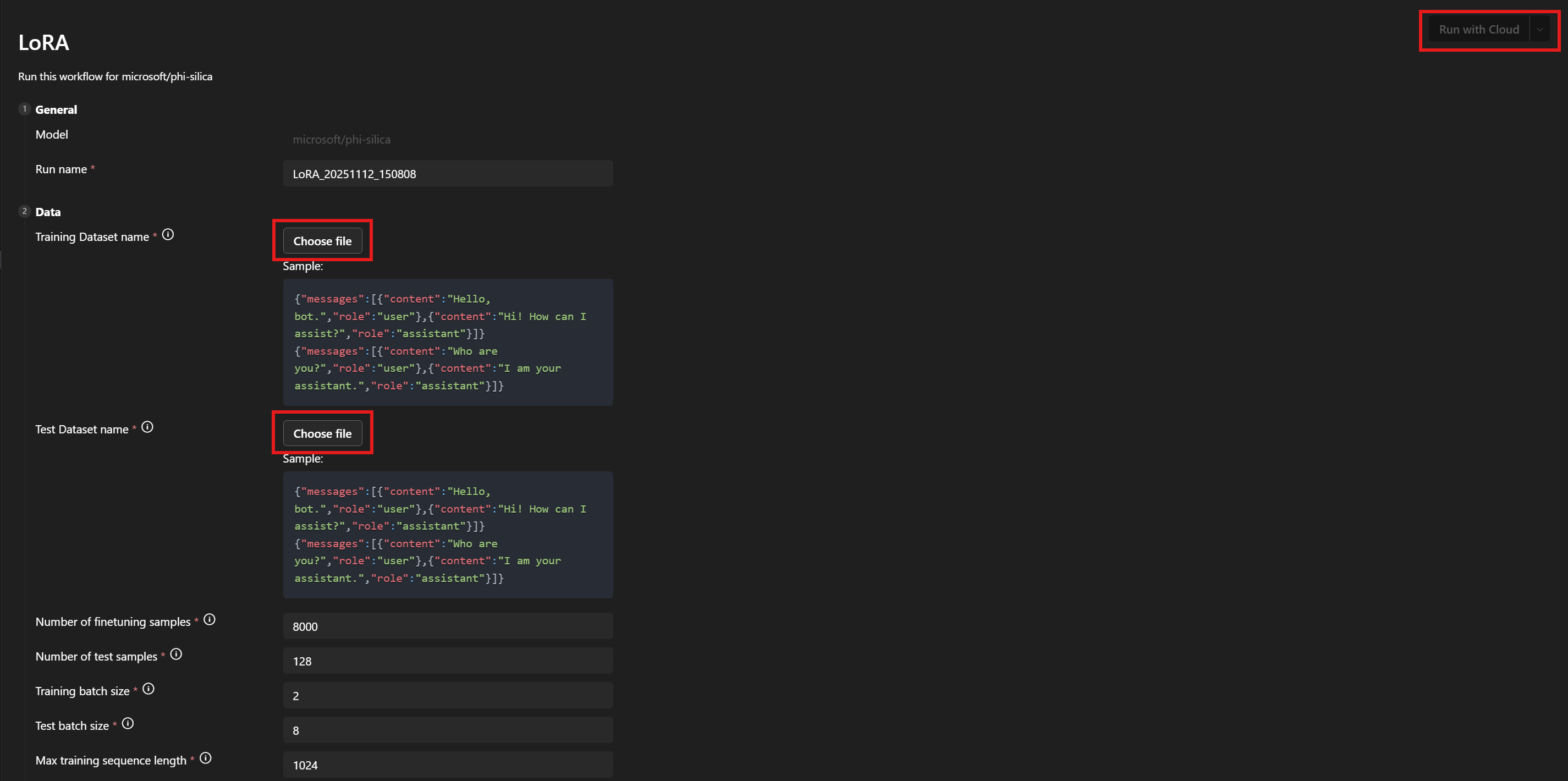
-
在 **資料 > 訓練資料集名稱** 和 **測試資料集名稱** 下,選擇您的
train.json和test.json檔案。 -
選擇 **使用雲執行**。
-
在對話方塊中,選擇用於訪問您 Azure 訂閱的 Microsoft 帳戶。
-
選擇完您的帳戶後,從訂閱下拉選單中選擇一個資源組。
-
您會注意到您的微調作業已成功啟動,並顯示作業狀態。
使用 **重新整理** 按鈕手動更新狀態。微調作業通常平均需要 45-60 分鐘才能完成。
-
作業完成後,您可以透過選擇 **下載** 來下載新訓練的 LoRA 介面卡,並透過選擇 **顯示指標** 來檢視微調指標。

LoRA 微調建議
超引數選擇
LoRA 微調的預設超引數設定應提供一個合理的基線微調值以供比較。我們已盡力找到適合大多數用例和資料集的預設值。
但是,如果您願意,我們仍保留了對引數進行掃描的靈活性。
訓練超引數
我們的標準引數搜尋空間將是
| 引數名稱 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 分佈 |
|---|---|---|---|
| learning_rate | 1e-4 | 1e-2 | Log-uniform |
| weight_decay | 1e-5 | 1e-1 | Log-uniform |
| adam_beta1 | 0.9 | 0.99 | Uniform |
| adam_beta2 | 0.9 | 0.999 | Uniform |
| adam_epsilon | 1e-9 | 1e-6 | Log-uniform |
| num_warmup_steps | 0 | 10000 | Uniform |
| lora_dropout | 0 | 0.5 | Uniform |
我們還會搜尋學習率排程器,選擇 linear_with_warmup 或 cosine_with_warmup 之一。如果 num_warmup_steps 引數設定為 0,則可以等效地使用線性或餘弦選項。
學習率、學習率排程器和預熱步數都相互關聯。固定其中兩個並改變第三個將使您更深入地瞭解它們如何改變資料集上訓練的輸出。
權重衰減和 LoRA Dropout 引數旨在幫助控制過擬合。如果您發現介面卡在訓練集和評估集上的泛化能力不佳,請嘗試增加這些引數的值。
adam_ parameters 影響 Adam 最佳化器在訓練步驟中的行為。有關該最佳化器的更多資訊,請參見例如 PyTorch 文件。
暴露的許多其他引數與其在 PEFT 庫中同名的對應引數類似。有關那些的更多資訊,請參閱 transformers 文件。
資料超引數
資料超引數 train_nsamples 和 test_nsamples 分別控制訓練和測試要使用的樣本數。使用更多的訓練集樣本通常是個好主意。使用更多的測試樣本可以得到更少噪聲的測試指標,但每次評估執行都會花費更長的時間。
train_batch_size 和 test_batch_size 引數分別控制訓練和測試中每個批次應使用的樣本數。您通常可以對測試使用比訓練更多的批次,因為執行測試樣本比訓練樣本佔用的 GPU 記憶體更少。
train_seqlen 和 test_seqlen 引數控制訓練和測試序列的長度。通常,越長越好,直到達到 GPU 記憶體限制。預設值應能提供良好的平衡。
選擇系統提示
我們發現用於選擇系統提示的有效策略是保持提示相對簡單(一兩句話),同時鼓勵模型以您想要的格式輸出。我們還發現,在訓練和推理中使用略有不同的系統提示可以提高結果。
您期望的輸出與基礎模型差異越大,系統提示就越能幫助您。
例如,如果您僅為基礎模型進行輕微的風格更改訓練,例如使用簡化語言以吸引年輕讀者,那麼您可能根本不需要系統提示。
但是,如果您的期望輸出具有更多結構,那麼您將需要使用系統提示來引導模型部分達到目標。因此,如果您需要一個帶有特定鍵的 JSON 表,系統提示的第一句話可以描述當模型以純語言響應時,響應應該是什麼樣子。第二句話可以進一步指定 JSON 表的格式。在訓練中使用第一句話,然後在推理中使用兩句話,可以為您提供想要的結果。
引數
所有可微調的引數列表附在此處。如果某個引數未出現在工作流頁面 UI 中,請手動將其新增到 <your_project_path>/<model_name>/lora/lora.yaml。
[
################## Basic config settings ##################
{
"groupId": "data",
"fields": [
{
"name": "system_prompt",
"type": "Optional",
"defaultValue": null,
"info": "Optional system prompt. If specified, the system prompt given here will be prepended to each example in the dataset as the system prompt when training the LoRA adapter. When running inference the same (or a very similar) system prompt should be used. Note: if a system prompt is specified in the training data, giving a system prompt here will overwrite the system prompt in the dataset.",
"label": "System prompt"
},
{
"name": "varied_seqlen",
"type": "bool",
"defaultValue": false,
"info": "Varied sequence lengths in the calibration data. If False (default), training examples will be concatenated together until they are finetune_[train/test]_seqlen tokens long. This makes memory usage more consistent and predictable. If True, each individual example will be truncated to finetune_[train/test]_seqlen tokens. This can sometimes give better training performance, but also gives unpredictable memory usage. It can cause `out of memory` errors mid training, if there are long training examples in your dataset.",
"label": "Allow varied sequence length in data"
},
{
"name": "finetune_dataset",
"type": "str",
"defaultValue": "wikitext2",
"info": "Dataset to finetune on.",
"label": "Dataset name or path"
},
{
"name": "finetune_train_nsamples",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 4096,
"info": "Number of samples to load from the train set for finetuning.",
"label": "Number of finetuning samples"
},
{
"name": "finetune_test_nsamples",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 128,
"info": "Number of samples to load from the test set for finetuning.",
"label": "Number of test samples"
},
{
"name": "finetune_train_batch_size",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 4,
"info": "Batch size for finetuning training.",
"label": "Training batch size"
},
{
"name": "finetune_test_batch_size",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 8,
"info": "Batch size for finetuning testing.",
"label": "Test batch size"
},
{
"name": "finetune_train_seqlen",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 2048,
"info": "Maximum sequence length for finetuning training. Longer sequences will be truncated.",
"label": "Max training sequence length"
},
{
"name": "finetune_test_seqlen",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 2048,
"info": "Maximum sequence length for finetuning testing. Longer sequences will be truncated.",
"label": "Max test sequence length"
}
]
},
{
"groupId": "finetuning",
"fields": [
{
"name": "early_stopping_patience",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 5,
"info": "Number of evaluations with no improvement after which training will be stopped.",
"label": "Early stopping patience"
},
{
"name": "epochs",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 1,
"info": "Number of total epochs to run.",
"label": "Epochs"
},
{
"name": "eval_steps",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 64,
"info": "Number of training steps to perform before each evaluation.",
"label": "Steps between evaluations"
},
{
"name": "save_steps",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 64,
"info": "Number of steps after which to save model checkpoint. This _must_ be a multiple of the number of steps between evaluations.",
"label": "Steps between checkpoints"
},
{
"name": "learning_rate",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 0.0002,
"info": "Learning rate for training.",
"label": "Learning rate"
},
{
"name": "lr_scheduler_type",
"type": "str",
"defaultValue": "linear",
"info": "Type of learning rate scheduler.",
"label": "Learning rate scheduler",
"optionValues": [
"linear",
"linear_with_warmup",
"cosine",
"cosine_with_warmup"
]
},
{
"name": "num_warmup_steps",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 400,
"info": "Number of warmup steps for learning rate scheduler. Only relevant for a _with_warmup scheduler.",
"label": "Scheduler warmup steps (if supported)"
}
]
}
################## Advanced config settings ##################
{
"groupId": "advanced",
"fields": [
{
"name": "seed",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 42,
"info": "Seed for sampling the data.",
"label": "Random seed"
},
{
"name": "evaluation_strategy",
"type": "str",
"defaultValue": "steps",
"info": "Evaluation strategy to use.",
"label": "Evaluation strategy",
"optionValues": [
"steps",
"epoch",
"no"
]
},
{
"name": "lora_dropout",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 0.1,
"info": "Dropout rate for LoRA.",
"label": "LoRA dropout"
},
{
"name": "adam_beta1",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 0.9,
"info": "Beta1 hyperparameter for Adam optimizer.",
"label": "Adam beta 1"
},
{
"name": "adam_beta2",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 0.95,
"info": "Beta2 hyperparameter for Adam optimizer.",
"label": "Adam beta 2"
},
{
"name": "adam_epsilon",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 1e-08,
"info": "Epsilon hyperparameter for Adam optimizer.",
"label": "Adam epsilon"
},
{
"name": "num_training_steps",
"type": "Optional",
"defaultValue": null,
"info": "The number of training steps there will be. If not set (recommended), this will be calculated internally.",
"label": "Number of training steps"
},
{
"name": "gradient_accumulation_steps",
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 1,
"info": "Number of updates steps to accumulate before performing a backward/update pass.",
"label": "gradient accumulation steps"
},
{
"name": "eval_accumulation_steps",
"type": "Optional",
"defaultValue": null,
"info": "Number of predictions steps to accumulate before moving the tensors to the CPU.",
"label": "eval accumulation steps"
},
{
"name": "eval_delay",
"type": "Optional",
"defaultValue": 0,
"info": "Number of epochs or steps to wait for before the first evaluation can be performed, depending on the eval_strategy.",
"label": "eval delay"
},
{
"name": "weight_decay",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 0.0,
"info": "Weight decay for AdamW if we apply some.",
"label": "weight decay"
},
{
"name": "max_grad_norm",
"type": "float",
"defaultValue": 1.0,
"info": "Max gradient norm.",
"label": "max grad norm"
},
{
"name": "gradient_checkpointing",
"type": "bool",
"defaultValue": false,
"info": "If True, use gradient checkpointing to save memory at the expense of slower backward pass.",
"label": "gradient checkpointing"
}
]
}
]
修改 Azure 訂閱和資源組
如果要修改之前設定的 Azure 訂閱和資源組,可以在 <your_project_path>/model_lab.workspace.provision.config 檔案中進行更新或刪除。
使用 Phi Silica LoRA 介面卡進行推理
Phi Silica API 是有限訪問功能的一部分(請參閱 LimitedAccessFeatures 類)。有關更多資訊或請求解鎖令牌,請使用 LAF 訪問令牌請求表。
目前,Phi Silica LoRA 介面卡的推理僅支援裝有 ARM 處理器的 Copilot+ PC。
使用 Windows AI API 進行推理:Phi Silica 與 LoRA 介面卡