語言伺服器擴充套件指南
如您在以程式設計方式實現語言功能主題中所見,可以透過直接使用languages.* API來實現語言功能。然而,語言伺服器擴充套件提供了實現此類語言支援的另一種方法。
本主題
- 解釋了語言伺服器擴充套件的優勢。
- 引導您使用
Microsoft/vscode-languageserver-node庫構建語言伺服器。您也可以直接跳轉到lsp-sample中的程式碼。
為什麼需要語言伺服器?
語言伺服器是一種特殊的 Visual Studio Code 擴充套件,它為許多程式語言提供了編輯體驗。透過語言伺服器,您可以實現自動完成、錯誤檢查(診斷)、跳轉到定義以及 VS Code 支援的許多其他語言功能。
然而,在 VS Code 中實現語言支援時,我們發現了三個常見問題:
首先,語言伺服器通常是用其原生程式語言實現的,這給將其整合到使用 Node.js 執行時的 VS Code 帶來了挑戰。
此外,語言功能可能非常消耗資源。例如,為了正確驗證一個檔案,語言伺服器需要解析大量檔案,為它們構建抽象語法樹,並執行靜態程式分析。這些操作可能會消耗大量的 CPU 和記憶體,我們需要確保 VS Code 的效能不受影響。
最後,將多個語言工具整合到多個程式碼編輯器中可能會涉及大量工作。從語言工具的角度來看,它們需要適應具有不同 API 的程式碼編輯器。從程式碼編輯器的角度來看,它們無法期望從語言工具獲得統一的 API。這使得在M個程式碼編輯器中實現M種語言的支援成為一項M * N的工作。
為了解決這些問題,微軟制定了語言伺服器協議,它標準化了語言工具和程式碼編輯器之間的通訊。這樣,語言伺服器就可以用任何語言實現,並在自己的程序中執行,以避免效能成本,因為它們透過語言伺服器協議與程式碼編輯器進行通訊。此外,任何符合 LSP 的語言工具都可以與多個符合 LSP 的程式碼編輯器整合,任何符合 LSP 的程式碼編輯器都可以輕鬆地選擇多個符合 LSP 的語言工具。LSP 對語言工具提供商和程式碼編輯器供應商來說都是一種雙贏!

在本指南中,我們將
- 解釋如何使用提供的Node SDK在 VS Code 中構建語言伺服器擴充套件。
- 解釋如何執行、除錯、記錄和測試語言伺服器擴充套件。
- 指向一些關於語言伺服器的高階主題。
實現語言伺服器
概述
在 VS Code 中,語言伺服器包含兩個部分:
- 語言客戶端:一個用 JavaScript / TypeScript 編寫的普通 VS Code 擴充套件。此擴充套件可以訪問所有VS Code 名稱空間 API。
- 語言伺服器:一個執行在獨立程序中的語言分析工具。
如上文簡要所述,在獨立程序中執行語言伺服器有兩個好處:
- 分析工具可以使用任何語言實現,只要它能按照語言伺服器協議與語言客戶端通訊。
- 由於語言分析工具通常對 CPU 和記憶體的佔用量很大,因此在獨立程序中執行它們可以避免效能成本。
這是 VS Code 執行兩個語言伺服器擴充套件的示意圖。HTML 語言客戶端和 PHP 語言客戶端是使用 TypeScript 編寫的普通 VS Code 擴充套件。它們各自例項化一個相應的語言伺服器,並透過 LSP 與之通訊。儘管 PHP 語言伺服器是用 PHP 編寫的,但它仍然可以透過 LSP 與 PHP 語言客戶端通訊。
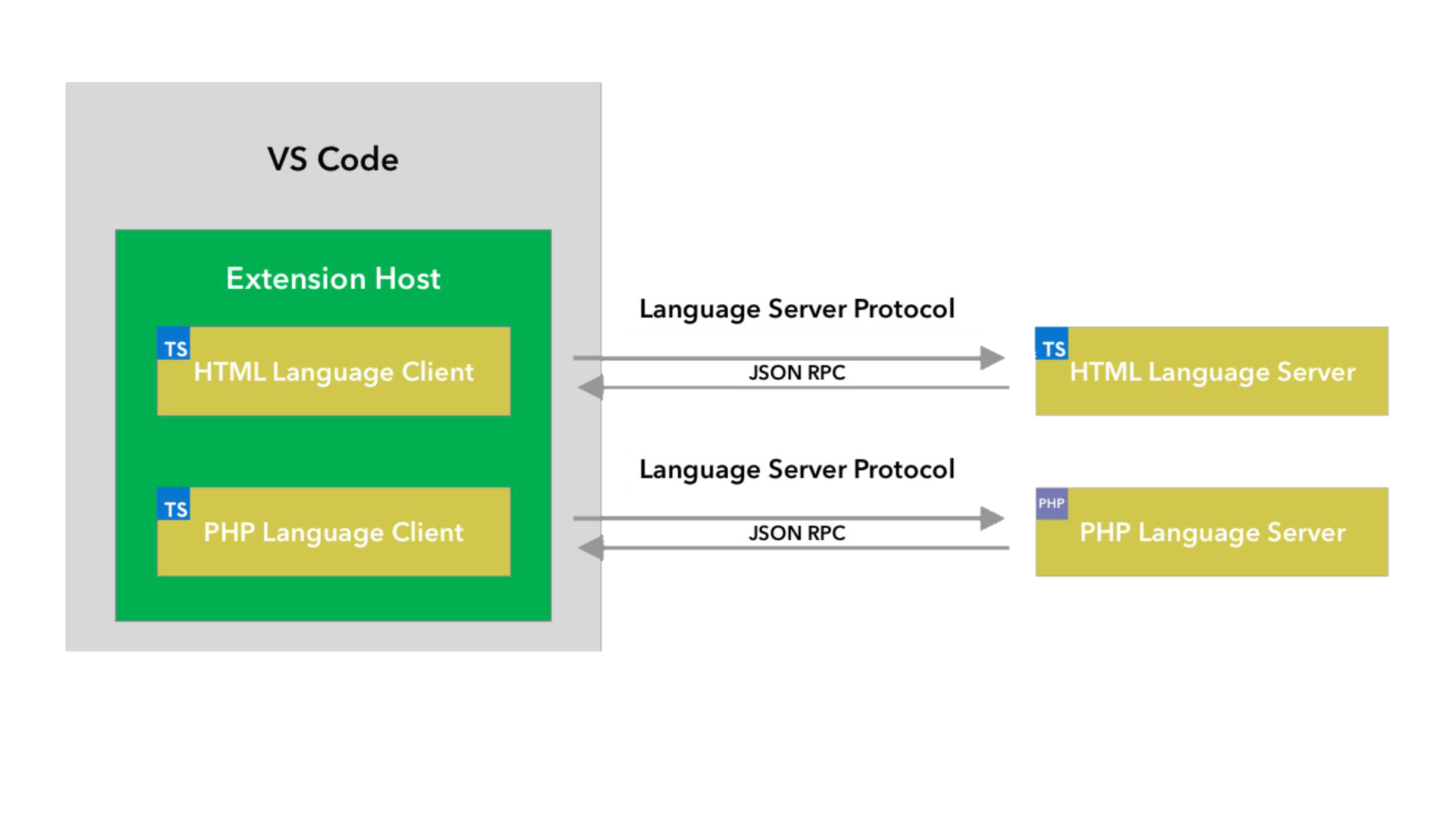
本指南將教您如何使用我們的Node SDK構建語言客戶端/伺服器。剩餘的文件假定您熟悉 VS Code 擴充套件 API。
LSP 示例 - 一個簡單的純文字檔案語言伺服器
讓我們構建一個簡單的語言伺服器擴充套件,為純文字檔案實現自動完成和診斷功能。我們還將介紹客戶端/伺服器之間的配置同步。
如果您希望直接檢視程式碼
- lsp-sample:本指南的詳細原始碼。
- lsp-multi-server-sample:這是lsp-sample的一個經過詳細文件記錄的高階版本,它為每個工作區資料夾啟動一個不同的伺服器例項,以支援 VS Code 中的多根工作區功能。
克隆儲存庫Microsoft/vscode-extension-samples並開啟示例。
> git clone https://github.com/microsoft/vscode-extension-samples.git
> cd vscode-extension-samples/lsp-sample
> npm install
> npm run compile
> code .
以上命令將安裝所有依賴項並開啟包含客戶端和伺服器程式碼的lsp-sample工作區。這是lsp-sample結構的大致概述。
.
├── client // Language Client
│ ├── src
│ │ ├── test // End to End tests for Language Client / Server
│ │ └── extension.ts // Language Client entry point
├── package.json // The extension manifest
└── server // Language Server
└── src
└── server.ts // Language Server entry point
解釋“語言客戶端”
讓我們首先看一下/package.json,它描述了語言客戶端的功能。有兩個有趣的節:
首先,檢視configuration部分。
"configuration": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Example configuration",
"properties": {
"languageServerExample.maxNumberOfProblems": {
"scope": "resource",
"type": "number",
"default": 100,
"description": "Controls the maximum number of problems produced by the server."
}
}
}
此部分將configuration設定貢獻給 VS Code。該示例將解釋這些設定如何在啟動時以及每次設定更改時傳送到語言伺服器。
注意:如果您的擴充套件與 VS Code 1.74.0 之前的版本相容,您必須在
/package.json的activationEvents欄位中宣告onLanguage:plaintext,以告知 VS Code 在開啟純文字檔案(例如副檔名為.txt的檔案)時立即啟用該擴充套件。"activationEvents": []
實際的語言客戶端原始碼和相應的package.json位於/client資料夾中。/client/package.json檔案中有趣的部分是它透過engines欄位引用vscode擴充套件宿主 API,並添加了對vscode-languageclient庫的依賴。
"engines": {
"vscode": "^1.52.0"
},
"dependencies": {
"vscode-languageclient": "^7.0.0"
}
如前所述,客戶端實現為一個普通的 VS Code 擴充套件,它可以訪問所有 VS Code 名稱空間 API。
以下是相應的 extension.ts 檔案的內容,它是lsp-sample擴充套件的入口。
import * as path from 'path';
import { workspace, ExtensionContext } from 'vscode';
import {
LanguageClient,
LanguageClientOptions,
ServerOptions,
TransportKind
} from 'vscode-languageclient/node';
let client: LanguageClient;
export function activate(context: ExtensionContext) {
// The server is implemented in node
let serverModule = context.asAbsolutePath(path.join('server', 'out', 'server.js'));
// The debug options for the server
// --inspect=6009: runs the server in Node's Inspector mode so VS Code can attach to the server for debugging
let debugOptions = { execArgv: ['--nolazy', '--inspect=6009'] };
// If the extension is launched in debug mode then the debug server options are used
// Otherwise the run options are used
let serverOptions: ServerOptions = {
run: { module: serverModule, transport: TransportKind.ipc },
debug: {
module: serverModule,
transport: TransportKind.ipc,
options: debugOptions
}
};
// Options to control the language client
let clientOptions: LanguageClientOptions = {
// Register the server for plain text documents
documentSelector: [{ scheme: 'file', language: 'plaintext' }],
synchronize: {
// Notify the server about file changes to '.clientrc files contained in the workspace
fileEvents: workspace.createFileSystemWatcher('**/.clientrc')
}
};
// Create the language client and start the client.
client = new LanguageClient(
'languageServerExample',
'Language Server Example',
serverOptions,
clientOptions
);
// Start the client. This will also launch the server
client.start();
}
export function deactivate(): Thenable<void> | undefined {
if (!client) {
return undefined;
}
return client.stop();
}
解釋“語言伺服器”
注意:從 GitHub 儲存庫克隆的“伺服器”實現包含最終的演練實現。要遵循演練,您可以建立一個新的
server.ts或修改克隆版本的內容。
在此示例中,伺服器也用 TypeScript 實現,並透過 Node.js 執行。由於 VS Code 本身就附帶了 Node.js 執行時,因此無需提供自己的執行時,除非您有特定的執行時要求。
語言伺服器的原始碼位於/server。伺服器的package.json檔案中有趣的節是:
"dependencies": {
"vscode-languageserver": "^7.0.0",
"vscode-languageserver-textdocument": "^1.0.1"
}
這會引入vscode-languageserver庫。
以下是一個使用提供的文字文件管理器實現的伺服器,該管理器透過始終將增量差異從 VS Code 傳送到伺服器來同步文字文件。
import {
createConnection,
TextDocuments,
Diagnostic,
DiagnosticSeverity,
ProposedFeatures,
InitializeParams,
DidChangeConfigurationNotification,
CompletionItem,
CompletionItemKind,
TextDocumentPositionParams,
TextDocumentSyncKind,
InitializeResult
} from 'vscode-languageserver/node';
import { TextDocument } from 'vscode-languageserver-textdocument';
// Create a connection for the server, using Node's IPC as a transport.
// Also include all preview / proposed LSP features.
let connection = createConnection(ProposedFeatures.all);
// Create a simple text document manager.
let documents: TextDocuments<TextDocument> = new TextDocuments(TextDocument);
let hasConfigurationCapability: boolean = false;
let hasWorkspaceFolderCapability: boolean = false;
let hasDiagnosticRelatedInformationCapability: boolean = false;
connection.onInitialize((params: InitializeParams) => {
let capabilities = params.capabilities;
// Does the client support the `workspace/configuration` request?
// If not, we fall back using global settings.
hasConfigurationCapability = !!(
capabilities.workspace && !!capabilities.workspace.configuration
);
hasWorkspaceFolderCapability = !!(
capabilities.workspace && !!capabilities.workspace.workspaceFolders
);
hasDiagnosticRelatedInformationCapability = !!(
capabilities.textDocument &&
capabilities.textDocument.publishDiagnostics &&
capabilities.textDocument.publishDiagnostics.relatedInformation
);
const result: InitializeResult = {
capabilities: {
textDocumentSync: TextDocumentSyncKind.Incremental,
// Tell the client that this server supports code completion.
completionProvider: {
resolveProvider: true
}
}
};
if (hasWorkspaceFolderCapability) {
result.capabilities.workspace = {
workspaceFolders: {
supported: true
}
};
}
return result;
});
connection.onInitialized(() => {
if (hasConfigurationCapability) {
// Register for all configuration changes.
connection.client.register(DidChangeConfigurationNotification.type, undefined);
}
if (hasWorkspaceFolderCapability) {
connection.workspace.onDidChangeWorkspaceFolders(_event => {
connection.console.log('Workspace folder change event received.');
});
}
});
// The example settings
interface ExampleSettings {
maxNumberOfProblems: number;
}
// The global settings, used when the `workspace/configuration` request is not supported by the client.
// Please note that this is not the case when using this server with the client provided in this example
// but could happen with other clients.
const defaultSettings: ExampleSettings = { maxNumberOfProblems: 1000 };
let globalSettings: ExampleSettings = defaultSettings;
// Cache the settings of all open documents
let documentSettings: Map<string, Thenable<ExampleSettings>> = new Map();
connection.onDidChangeConfiguration(change => {
if (hasConfigurationCapability) {
// Reset all cached document settings
documentSettings.clear();
} else {
globalSettings = <ExampleSettings>(
(change.settings.languageServerExample || defaultSettings)
);
}
// Revalidate all open text documents
documents.all().forEach(validateTextDocument);
});
function getDocumentSettings(resource: string): Thenable<ExampleSettings> {
if (!hasConfigurationCapability) {
return Promise.resolve(globalSettings);
}
let result = documentSettings.get(resource);
if (!result) {
result = connection.workspace.getConfiguration({
scopeUri: resource,
section: 'languageServerExample'
});
documentSettings.set(resource, result);
}
return result;
}
// Only keep settings for open documents
documents.onDidClose(e => {
documentSettings.delete(e.document.uri);
});
// The content of a text document has changed. This event is emitted
// when the text document first opened or when its content has changed.
documents.onDidChangeContent(change => {
validateTextDocument(change.document);
});
async function validateTextDocument(textDocument: TextDocument): Promise<void> {
// In this simple example we get the settings for every validate run.
let settings = await getDocumentSettings(textDocument.uri);
// The validator creates diagnostics for all uppercase words length 2 and more
let text = textDocument.getText();
let pattern = /\b[A-Z]{2,}\b/g;
let m: RegExpExecArray | null;
let problems = 0;
let diagnostics: Diagnostic[] = [];
while ((m = pattern.exec(text)) && problems < settings.maxNumberOfProblems) {
problems++;
let diagnostic: Diagnostic = {
severity: DiagnosticSeverity.Warning,
range: {
start: textDocument.positionAt(m.index),
end: textDocument.positionAt(m.index + m[0].length)
},
message: `${m[0]} is all uppercase.`,
source: 'ex'
};
if (hasDiagnosticRelatedInformationCapability) {
diagnostic.relatedInformation = [
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Spelling matters'
},
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Particularly for names'
}
];
}
diagnostics.push(diagnostic);
}
// Send the computed diagnostics to VS Code.
connection.sendDiagnostics({ uri: textDocument.uri, diagnostics });
}
connection.onDidChangeWatchedFiles(_change => {
// Monitored files have change in VS Code
connection.console.log('We received a file change event');
});
// This handler provides the initial list of the completion items.
connection.onCompletion(
(_textDocumentPosition: TextDocumentPositionParams): CompletionItem[] => {
// The pass parameter contains the position of the text document in
// which code complete got requested. For the example we ignore this
// info and always provide the same completion items.
return [
{
label: 'TypeScript',
kind: CompletionItemKind.Text,
data: 1
},
{
label: 'JavaScript',
kind: CompletionItemKind.Text,
data: 2
}
];
}
);
// This handler resolves additional information for the item selected in
// the completion list.
connection.onCompletionResolve(
(item: CompletionItem): CompletionItem => {
if (item.data === 1) {
item.detail = 'TypeScript details';
item.documentation = 'TypeScript documentation';
} else if (item.data === 2) {
item.detail = 'JavaScript details';
item.documentation = 'JavaScript documentation';
}
return item;
}
);
// Make the text document manager listen on the connection
// for open, change and close text document events
documents.listen(connection);
// Listen on the connection
connection.listen();
新增簡單的驗證
為了向伺服器新增文件驗證,我們向文字文件管理器添加了一個偵聽器,該偵聽器在文字文件內容更改時被呼叫。然後,由伺服器決定何時是驗證文件的最佳時間。在示例實現中,伺服器會驗證純文字文件,並標記所有使用全大寫的單詞。相應的程式碼片段如下所示:
// The content of a text document has changed. This event is emitted
// when the text document first opened or when its content has changed.
documents.onDidChangeContent(async change => {
let textDocument = change.document;
// In this simple example we get the settings for every validate run.
let settings = await getDocumentSettings(textDocument.uri);
// The validator creates diagnostics for all uppercase words length 2 and more
let text = textDocument.getText();
let pattern = /\b[A-Z]{2,}\b/g;
let m: RegExpExecArray | null;
let problems = 0;
let diagnostics: Diagnostic[] = [];
while ((m = pattern.exec(text)) && problems < settings.maxNumberOfProblems) {
problems++;
let diagnostic: Diagnostic = {
severity: DiagnosticSeverity.Warning,
range: {
start: textDocument.positionAt(m.index),
end: textDocument.positionAt(m.index + m[0].length)
},
message: `${m[0]} is all uppercase.`,
source: 'ex'
};
if (hasDiagnosticRelatedInformationCapability) {
diagnostic.relatedInformation = [
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Spelling matters'
},
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Particularly for names'
}
];
}
diagnostics.push(diagnostic);
}
// Send the computed diagnostics to VS Code.
connection.sendDiagnostics({ uri: textDocument.uri, diagnostics });
});
診斷技巧與竅門
- 如果開始和結束位置相同,VS Code 將在該位置用波浪線劃出單詞。
- 如果您想用波浪線劃出直到行尾,請將結束位置的字元設定為 Number.MAX_VALUE。
要執行語言伺服器,請執行以下步驟:
- 按⇧⌘B (Windows、Linux Ctrl+Shift+B)啟動構建任務。該任務將編譯客戶端和伺服器。
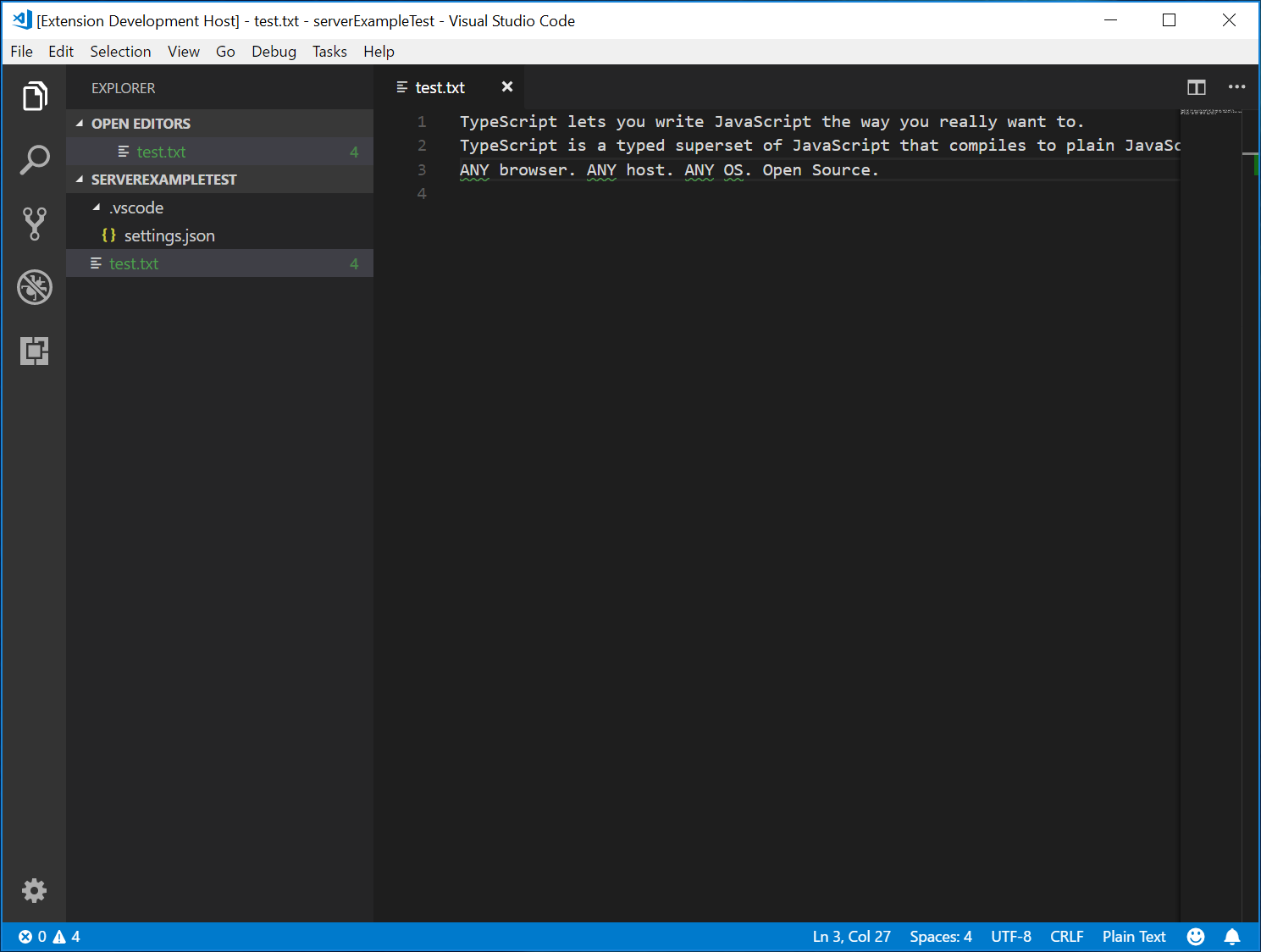
- 開啟執行檢視,選擇啟動客戶端啟動配置,然後按開始除錯按鈕,啟動另一個 VS Code 的擴充套件開發主機例項,該例項將執行擴充套件程式碼。
- 在根資料夾中建立一個
test.txt檔案,並貼上以下內容:
TypeScript lets you write JavaScript the way you really want to.
TypeScript is a typed superset of JavaScript that compiles to plain JavaScript.
ANY browser. ANY host. ANY OS. Open Source.
然後,擴充套件開發主機例項將如下所示:
同時除錯客戶端和伺服器
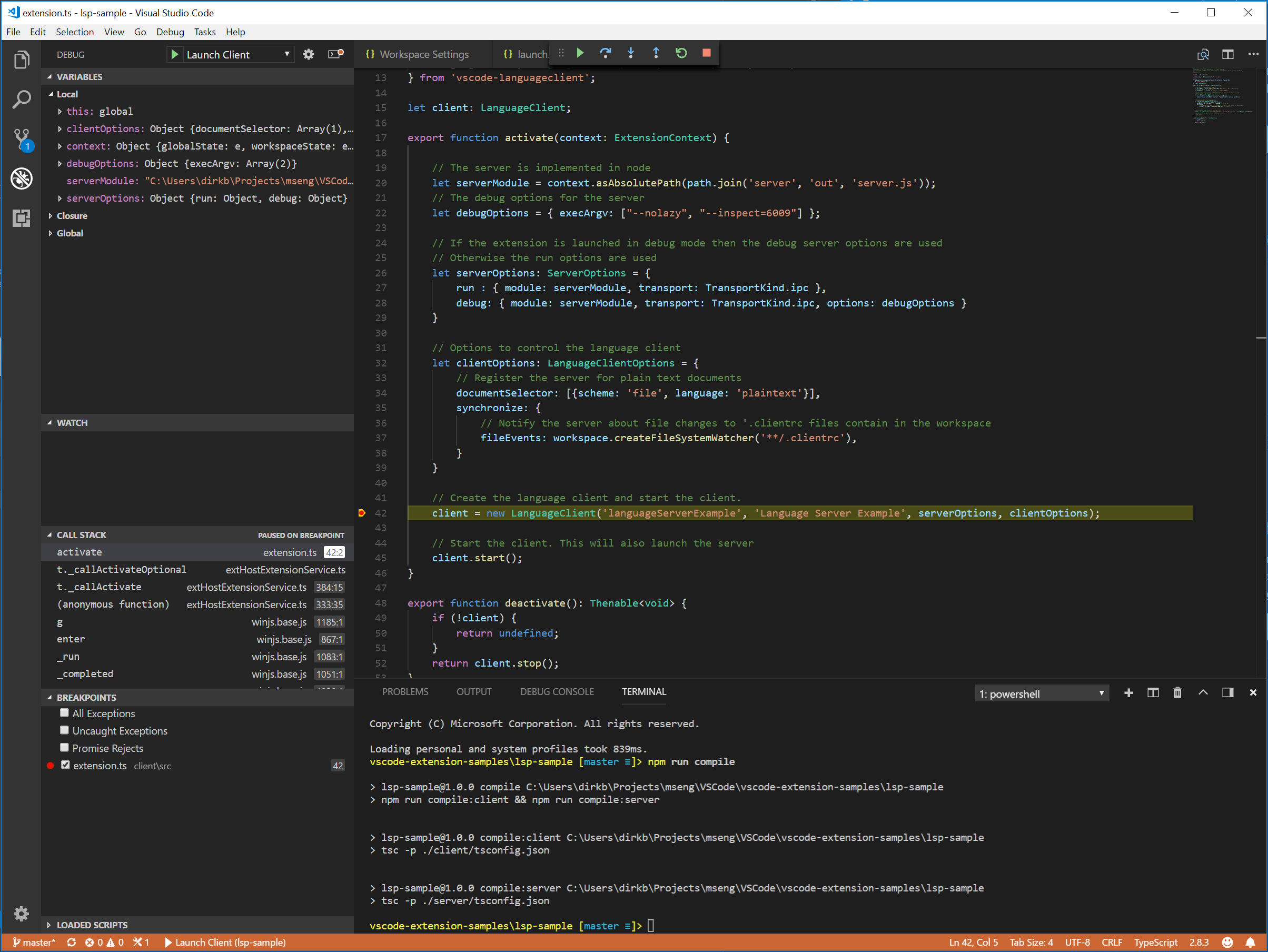
除錯客戶端程式碼與除錯普通擴充套件一樣簡單。在客戶端程式碼中設定斷點,然後按F5除錯擴充套件。
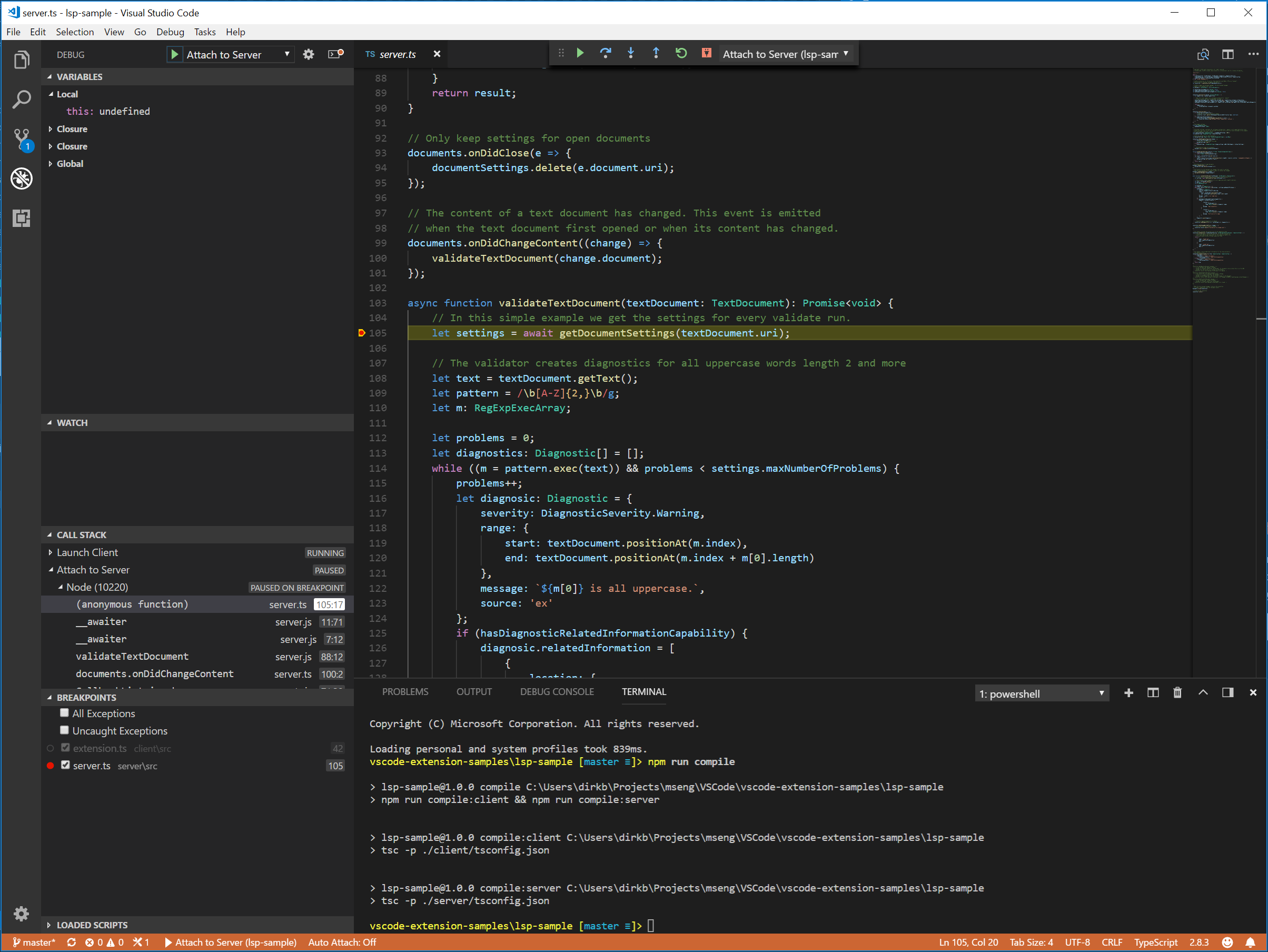
由於伺服器是由擴充套件(客戶端)中執行的LanguageClient啟動的,因此我們需要將偵錯程式附加到正在執行的伺服器。為此,切換到執行和除錯檢視,選擇附加到伺服器啟動配置,然後按F5。這將把偵錯程式附加到伺服器。
語言伺服器的日誌支援
如果您使用vscode-languageclient來實現客戶端,您可以指定一個設定[langId].trace.server,它指示客戶端將語言客戶端/伺服器之間的通訊記錄到語言客戶端name的一個通道中。
對於lsp-sample,您可以設定此選項:"languageServerExample.trace.server": "verbose"。現在轉到“Language Server Example”通道。您應該能看到日誌。
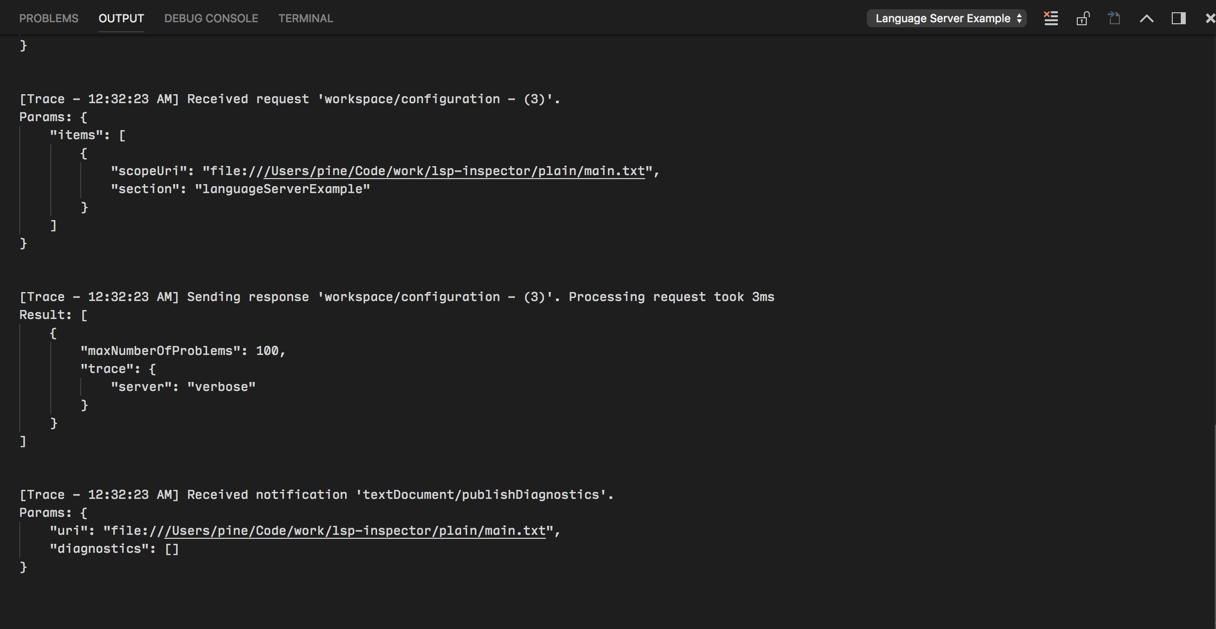
在伺服器中使用配置設定
在編寫擴充套件的客戶端部分時,我們已經定義了一個設定來控制報告的問題的最大數量。我們還在伺服器端編寫了程式碼來讀取客戶端的這些設定。
function getDocumentSettings(resource: string): Thenable<ExampleSettings> {
if (!hasConfigurationCapability) {
return Promise.resolve(globalSettings);
}
let result = documentSettings.get(resource);
if (!result) {
result = connection.workspace.getConfiguration({
scopeUri: resource,
section: 'languageServerExample'
});
documentSettings.set(resource, result);
}
return result;
}
現在我們只需要在伺服器端監聽配置更改,如果設定發生更改,則重新驗證開啟的文字文件。為了能夠重用文件更改事件處理中的驗證邏輯,我們將程式碼提取到一個validateTextDocument函式中,並修改程式碼以遵循maxNumberOfProblems變數。
async function validateTextDocument(textDocument: TextDocument): Promise<void> {
// In this simple example we get the settings for every validate run.
let settings = await getDocumentSettings(textDocument.uri);
// The validator creates diagnostics for all uppercase words length 2 and more
let text = textDocument.getText();
let pattern = /\b[A-Z]{2,}\b/g;
let m: RegExpExecArray | null;
let problems = 0;
let diagnostics: Diagnostic[] = [];
while ((m = pattern.exec(text)) && problems < settings.maxNumberOfProblems) {
problems++;
let diagnostic: Diagnostic = {
severity: DiagnosticSeverity.Warning,
range: {
start: textDocument.positionAt(m.index),
end: textDocument.positionAt(m.index + m[0].length)
},
message: `${m[0]} is all uppercase.`,
source: 'ex'
};
if (hasDiagnosticRelatedInformationCapability) {
diagnostic.relatedInformation = [
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Spelling matters'
},
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Particularly for names'
}
];
}
diagnostics.push(diagnostic);
}
// Send the computed diagnostics to VS Code.
connection.sendDiagnostics({ uri: textDocument.uri, diagnostics });
}
透過在連線中新增一個配置更改的通知處理程式來處理配置更改。相應的程式碼如下所示:
connection.onDidChangeConfiguration(change => {
if (hasConfigurationCapability) {
// Reset all cached document settings
documentSettings.clear();
} else {
globalSettings = <ExampleSettings>(
(change.settings.languageServerExample || defaultSettings)
);
}
// Revalidate all open text documents
documents.all().forEach(validateTextDocument);
});
重新啟動客戶端並將設定更改為最多報告 1 個問題,將導致以下驗證:
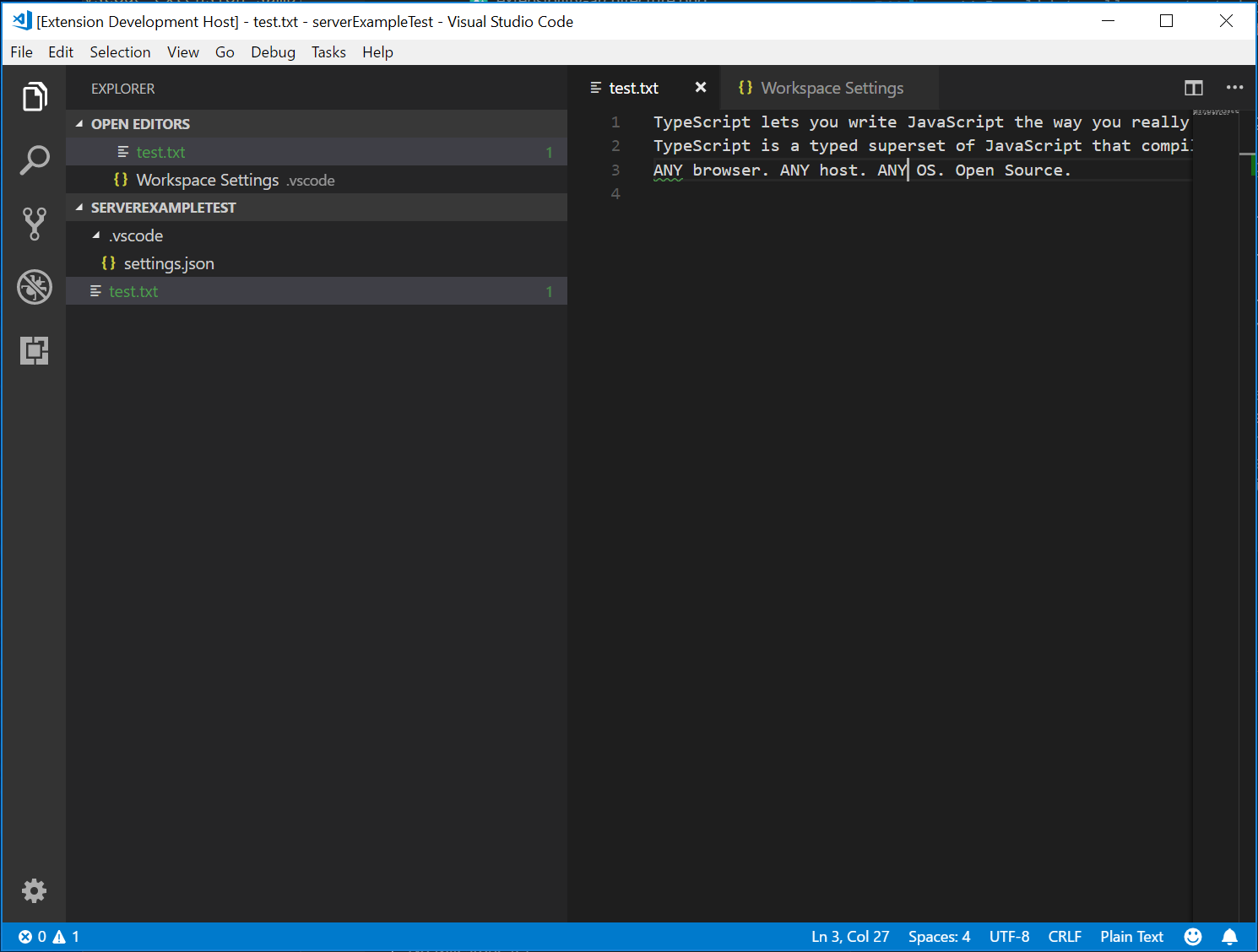
新增其他語言功能
語言伺服器通常實現的第一個有趣功能是文件驗證。從這個意義上說,即使是 linter 也被視為語言伺服器,並且在 VS Code 中,linter 通常作為語言伺服器實現(例如eslint和jshint)。但語言伺服器還有更多功能。它們可以提供程式碼補全、查詢所有引用或跳轉到定義。下面的示例程式碼向伺服器添加了程式碼補全功能。它建議“TypeScript”和“JavaScript”這兩個詞。
// This handler provides the initial list of the completion items.
connection.onCompletion(
(_textDocumentPosition: TextDocumentPositionParams): CompletionItem[] => {
// The pass parameter contains the position of the text document in
// which code complete got requested. For the example we ignore this
// info and always provide the same completion items.
return [
{
label: 'TypeScript',
kind: CompletionItemKind.Text,
data: 1
},
{
label: 'JavaScript',
kind: CompletionItemKind.Text,
data: 2
}
];
}
);
// This handler resolves additional information for the item selected in
// the completion list.
connection.onCompletionResolve(
(item: CompletionItem): CompletionItem => {
if (item.data === 1) {
item.detail = 'TypeScript details';
item.documentation = 'TypeScript documentation';
} else if (item.data === 2) {
item.detail = 'JavaScript details';
item.documentation = 'JavaScript documentation';
}
return item;
}
);
data欄位用於在解析處理程式中唯一標識一個補全項。data 屬性對協議是透明的。由於底層訊息傳遞協議是基於 JSON 的,因此 data 欄位只能包含可與 JSON 相互序列化的資料。
唯一需要做的就是告訴 VS Code 伺服器支援程式碼補全請求。為此,在初始化處理程式中標記相應的 capability。
connection.onInitialize((params): InitializeResult => {
...
return {
capabilities: {
...
// Tell the client that the server supports code completion
completionProvider: {
resolveProvider: true
}
}
};
});
下圖顯示了在純文字檔案上執行的完成程式碼。
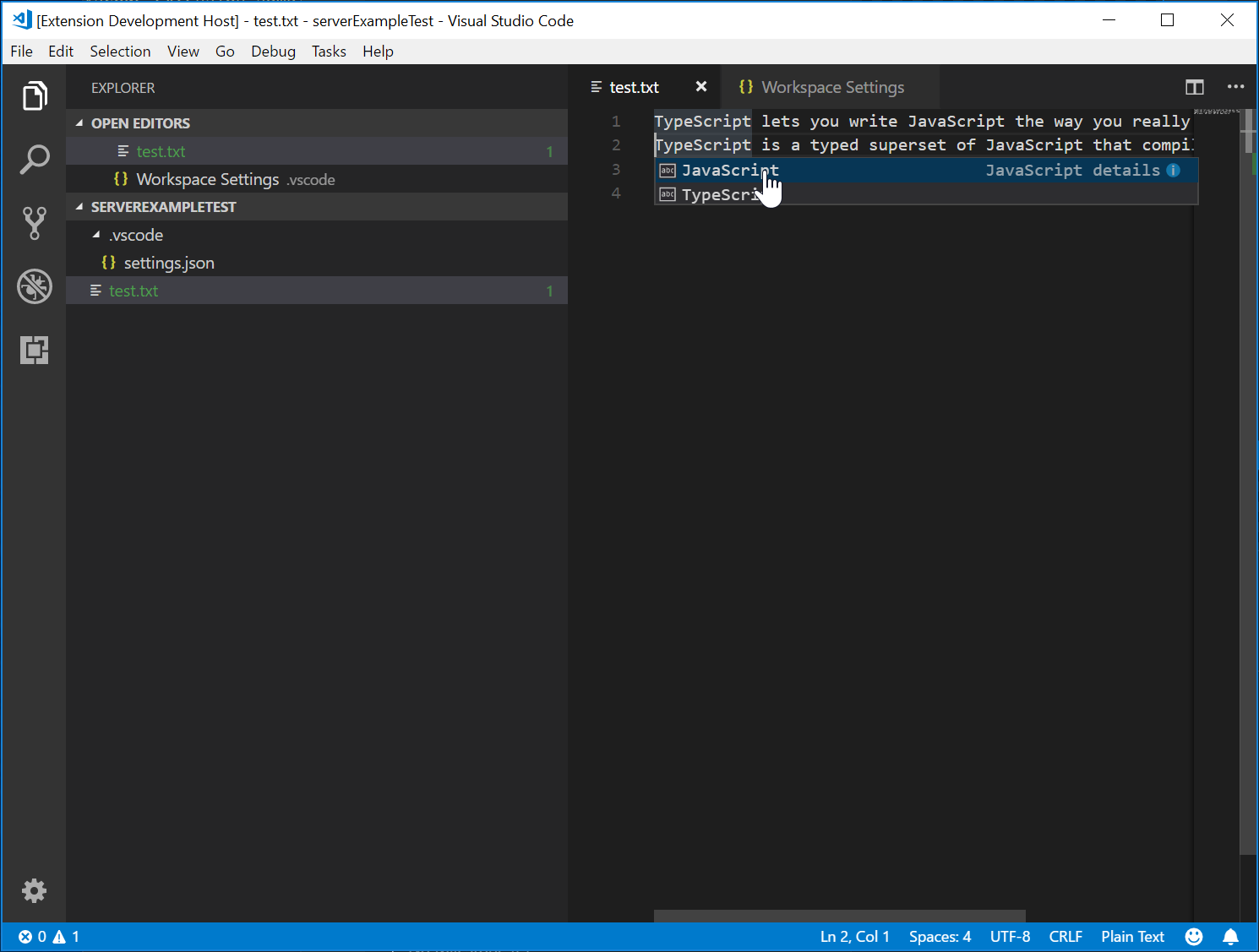
測試語言伺服器
要建立高質量的語言伺服器,我們需要構建一個涵蓋其功能的良好測試套件。測試語言伺服器有兩種常用方法:
- 單元測試:如果您想透過模擬傳送給語言伺服器的所有資訊來測試語言伺服器中的特定功能,這將非常有用。VS Code 的HTML / CSS / JSON語言伺服器採用了這種測試方法。LSP npm 模組也採用了這種方法。有關使用 npm 協議模組編寫的一些單元測試,請參閱此處。
- 端到端測試:這類似於VS Code 擴充套件測試。此方法的優點是它透過例項化帶有工作區的 VS Code 例項、開啟檔案、啟用語言客戶端/伺服器並執行VS Code 命令來執行測試。如果您有難以或不可能模擬的檔案、設定或依賴項(例如
node_modules),則此方法更優越。流行的Python擴展采用了這種測試方法。
您可以使用您選擇的任何測試框架進行單元測試。這裡我們描述瞭如何為語言伺服器擴充套件進行端到端測試。
開啟.vscode/launch.json,您會找到一個E2E測試目標。
{
"name": "Language Server E2E Test",
"type": "extensionHost",
"request": "launch",
"runtimeExecutable": "${execPath}",
"args": [
"--extensionDevelopmentPath=${workspaceRoot}",
"--extensionTestsPath=${workspaceRoot}/client/out/test/index",
"${workspaceRoot}/client/testFixture"
],
"outFiles": ["${workspaceRoot}/client/out/test/**/*.js"]
}
如果您執行此除錯目標,它將啟動一個 VS Code 例項,並將client/testFixture作為活動工作區。然後 VS Code 將繼續執行client/src/test中的所有測試。作為除錯技巧,您可以在client/src/test中的 TypeScript 檔案中設定斷點,這些斷點將被命中。
讓我們看一下completion.test.ts檔案。
import * as vscode from 'vscode';
import * as assert from 'assert';
import { getDocUri, activate } from './helper';
suite('Should do completion', () => {
const docUri = getDocUri('completion.txt');
test('Completes JS/TS in txt file', async () => {
await testCompletion(docUri, new vscode.Position(0, 0), {
items: [
{ label: 'JavaScript', kind: vscode.CompletionItemKind.Text },
{ label: 'TypeScript', kind: vscode.CompletionItemKind.Text }
]
});
});
});
async function testCompletion(
docUri: vscode.Uri,
position: vscode.Position,
expectedCompletionList: vscode.CompletionList
) {
await activate(docUri);
// Executing the command `vscode.executeCompletionItemProvider` to simulate triggering completion
const actualCompletionList = (await vscode.commands.executeCommand(
'vscode.executeCompletionItemProvider',
docUri,
position
)) as vscode.CompletionList;
assert.ok(actualCompletionList.items.length >= 2);
expectedCompletionList.items.forEach((expectedItem, i) => {
const actualItem = actualCompletionList.items[i];
assert.equal(actualItem.label, expectedItem.label);
assert.equal(actualItem.kind, expectedItem.kind);
});
}
在此測試中,我們:
- 啟用擴充套件。
- 執行
vscode.executeCompletionItemProvider命令,提供 URI 和位置,以模擬補全觸發。 - 將返回的補全項與我們預期的補全項進行斷言。
讓我們更深入地研究一下activate(docURI)函式。它定義在client/src/test/helper.ts中。
import * as vscode from 'vscode';
import * as path from 'path';
export let doc: vscode.TextDocument;
export let editor: vscode.TextEditor;
export let documentEol: string;
export let platformEol: string;
/**
* Activates the vscode.lsp-sample extension
*/
export async function activate(docUri: vscode.Uri) {
// The extensionId is `publisher.name` from package.json
const ext = vscode.extensions.getExtension('vscode-samples.lsp-sample')!;
await ext.activate();
try {
doc = await vscode.workspace.openTextDocument(docUri);
editor = await vscode.window.showTextDocument(doc);
await sleep(2000); // Wait for server activation
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
}
async function sleep(ms: number) {
return new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
}
在啟用部分,我們:
- 使用
{publisher.name}.{extensionId}(如package.json中定義的)獲取擴充套件。 - 開啟指定的文件,並在活動文字編輯器中顯示它。
- 等待 2 秒,以確保語言伺服器已例項化。
在準備工作完成後,我們可以執行每個語言功能對應的VS Code 命令,並斷言返回的結果。
還有一個測試涵蓋了我們剛剛實現的診斷功能。您可以在client/src/test/diagnostics.test.ts中找到它。
高階主題
到目前為止,本指南涵蓋了:
- 語言伺服器和語言伺服器協議的簡要概述。
- VS Code 中語言伺服器擴充套件的架構。
- lsp-sample擴充套件,以及如何開發/除錯/檢查/測試它。
有一些更高階的主題我們無法包含在本指南中。我們將提供這些資源的連結,供您進一步學習語言伺服器開發。
其他語言伺服器功能
除了程式碼補全之外,語言伺服器目前支援以下語言功能:
- 文件高亮:高亮顯示文字文件中的所有“相等”符號。
- 懸停:提供所選文字文件符號的懸停資訊。
- 簽名幫助:提供所選文字文件符號的簽名幫助。
- 跳轉到定義:為所選文字文件符號提供跳轉到定義的支援。
- 跳轉到型別定義:為所選文字文件符號提供跳轉到型別/介面定義的支援。
- 跳轉到實現:為所選文字文件符號提供跳轉到實現定義的支援。
- 查詢引用:查詢所選文字文件符號在整個專案中的所有引用。
- 列出文件符號:列出文件中定義的所有符號。
- 列出工作區符號:列出專案中的所有符號。
- 程式碼操作:計算給定文字文件和範圍要執行的命令(通常是格式化/重構)。
- CodeLens:計算給定文字文件的 CodeLens 統計資訊。
- 文件格式化:包括整個文件、文件範圍的格式化以及輸入時格式化。
- 重新命名:專案範圍內的符號重新命名。
- 文件連結:計算和解析文件中的連結。
- 文件顏色:計算和解析文件中的顏色,以便在編輯器中提供顏色選擇器。
以程式設計方式實現語言功能主題描述了上述每種語言功能,並提供了關於如何透過語言伺服器協議或直接從擴充套件中使用可擴充套件性 API 來實現它們的指導。
增量文字文件同步
該示例使用vscode-languageserver模組提供的簡單文字文件管理器來同步 VS Code 和語言伺服器之間的文件。
這有兩個缺點:
- 傳輸大量資料,因為整個文字文件的內容會反覆傳送到伺服器。
- 如果使用現有的語言庫,這些庫通常支援增量文件更新,以避免不必要的解析和抽象語法樹建立。
因此,該協議也支援增量文件同步。
為了利用增量文件同步,伺服器需要安裝三個通知處理程式:
- onDidOpenTextDocument:在 VS Code 中開啟文字文件時呼叫。
- onDidChangeTextDocument:在 VS Code 中文字文件內容更改時呼叫。
- onDidCloseTextDocument:在 VS Code 中關閉文字文件時呼叫。
下面的程式碼片段說明了如何在連線上掛接這些通知處理程式,以及如何在初始化時返回正確的 capability。
connection.onInitialize((params): InitializeResult => {
...
return {
capabilities: {
// Enable incremental document sync
textDocumentSync: TextDocumentSyncKind.Incremental,
...
}
};
});
connection.onDidOpenTextDocument((params) => {
// A text document was opened in VS Code.
// params.uri uniquely identifies the document. For documents stored on disk, this is a file URI.
// params.text the initial full content of the document.
});
connection.onDidChangeTextDocument((params) => {
// The content of a text document has change in VS Code.
// params.uri uniquely identifies the document.
// params.contentChanges describe the content changes to the document.
});
connection.onDidCloseTextDocument((params) => {
// A text document was closed in VS Code.
// params.uri uniquely identifies the document.
});
/*
Make the text document manager listen on the connection
for open, change and close text document events.
Comment out this line to allow `connection.onDidOpenTextDocument`,
`connection.onDidChangeTextDocument`, and `connection.onDidCloseTextDocument` to handle the events
*/
// documents.listen(connection);
直接使用 VS Code API 實現語言功能
儘管語言伺服器有很多好處,但它們並不是擴充套件 VS Code 編輯功能的唯一選擇。在您想為某種型別的文件新增一些簡單的語言功能時,請考慮使用vscode.languages.register[LANGUAGE_FEATURE]Provider作為一種選擇。
這裡有一個使用vscode.languages.registerCompletionItemProvider為純文字檔案新增一些程式碼片段作為補全的completions-sample。
更多說明 VS Code API 用法的示例可以在https://github.com/microsoft/vscode-extension-samples找到。
容錯解析器用於語言伺服器
大多數時候,編輯器中的程式碼是不完整的、語法不正確的,但開發人員仍然期望自動完成和其他語言功能正常工作。因此,容錯解析器對於語言伺服器是必需的:解析器可以從不完整的程式碼生成有意義的 AST,語言伺服器基於 AST 提供語言功能。
當我們改進 VS Code 中的 PHP 支援時,我們意識到官方 PHP 解析器不是容錯的,不能直接在語言伺服器中重用。因此,我們開發了Microsoft/tolerant-php-parser,並留下了詳細的筆記,這可能有助於需要實現容錯解析器的語言伺服器作者。
常見問題
當我嘗試附加到伺服器時,出現“無法連線到執行時程序(超時 5000 毫秒)”?
如果您在嘗試附加偵錯程式時伺服器未執行,您將看到此超時錯誤。客戶端會啟動語言伺服器,因此請確保您已啟動客戶端以執行伺服器。您可能還需要停用客戶端斷點,以防它們干擾伺服器啟動。
我已閱讀本指南和LSP 規範,但我仍有未解決的問題。在哪裡可以獲得幫助?
請在https://github.com/microsoft/language-server-protocol上開啟一個問題。