教程:使用語言模型 API 生成 AI 程式碼註釋
在本教程中,你將學習如何建立一個 VS Code 擴充套件來構建一個 AI 程式碼導師。你將使用語言模型 (LM) API 來生成改進程式碼的建議,並利用 VS Code 擴充套件 API 將其無縫整合到編輯器中,作為使用者可以懸停以獲取更多資訊的內聯註釋。完成本教程後,你將知道如何在 VS Code 中實現自定義 AI 功能。

先決條件
要完成本教程,你需要以下工具和賬戶
搭建擴充套件框架
首先,使用 Yeoman 和 VS Code 擴充套件生成器來搭建一個 TypeScript 或 JavaScript 專案,為開發做好準備。
npx --package yo --package generator-code -- yo code
選擇以下選項以完成新擴充套件嚮導...
# ? What type of extension do you want to create? New Extension (TypeScript)
# ? What's the name of your extension? Code Tutor
### Press <Enter> to choose default for all options below ###
# ? What's the identifier of your extension? code-tutor
# ? What's the description of your extension? LEAVE BLANK
# ? Initialize a git repository? Yes
# ? Bundle the source code with webpack? No
# ? Which package manager to use? npm
# ? Do you want to open the new folder with Visual Studio Code? Open with `code`
修改 package.json 檔案以包含正確的命令
搭建的專案在 package.json 檔案中包含一個名為 "helloWorld" 的命令。該命令是你的擴充套件安裝後在命令面板中顯示的內容。
"contributes": {
"commands": [
{
"command": "code-tutor.helloWorld",
"title": "Hello World"
}
]
}
由於我們要建立一個程式碼導師擴充套件,它將為程式碼行添加註釋,我們需要一個命令來允許使用者開啟和關閉這些註釋。更新 command 和 title 屬性
"contributes": {
"commands": [
{
"command": "code-tutor.annotate",
"title": "Toggle Tutor Annotations"
}
]
}
雖然 package.json 定義了擴充套件的命令和 UI 元素,但 src/extension.ts 檔案是你放置應為這些命令執行的程式碼的地方。
開啟 src/extension.ts 檔案,並修改 registerCommand 方法,使其與 package.json 檔案中的 command 屬性匹配。
const disposable = vscode.commands.registerCommand('code-tutor.annotate', () => {
透過按 F5 執行擴充套件。這將開啟一個新的 VS Code 例項,其中已安裝了該擴充套件。透過按 ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P) 開啟命令面板,然後搜尋 "tutor"。你應該會看到 "Tutor Annotations" 命令。
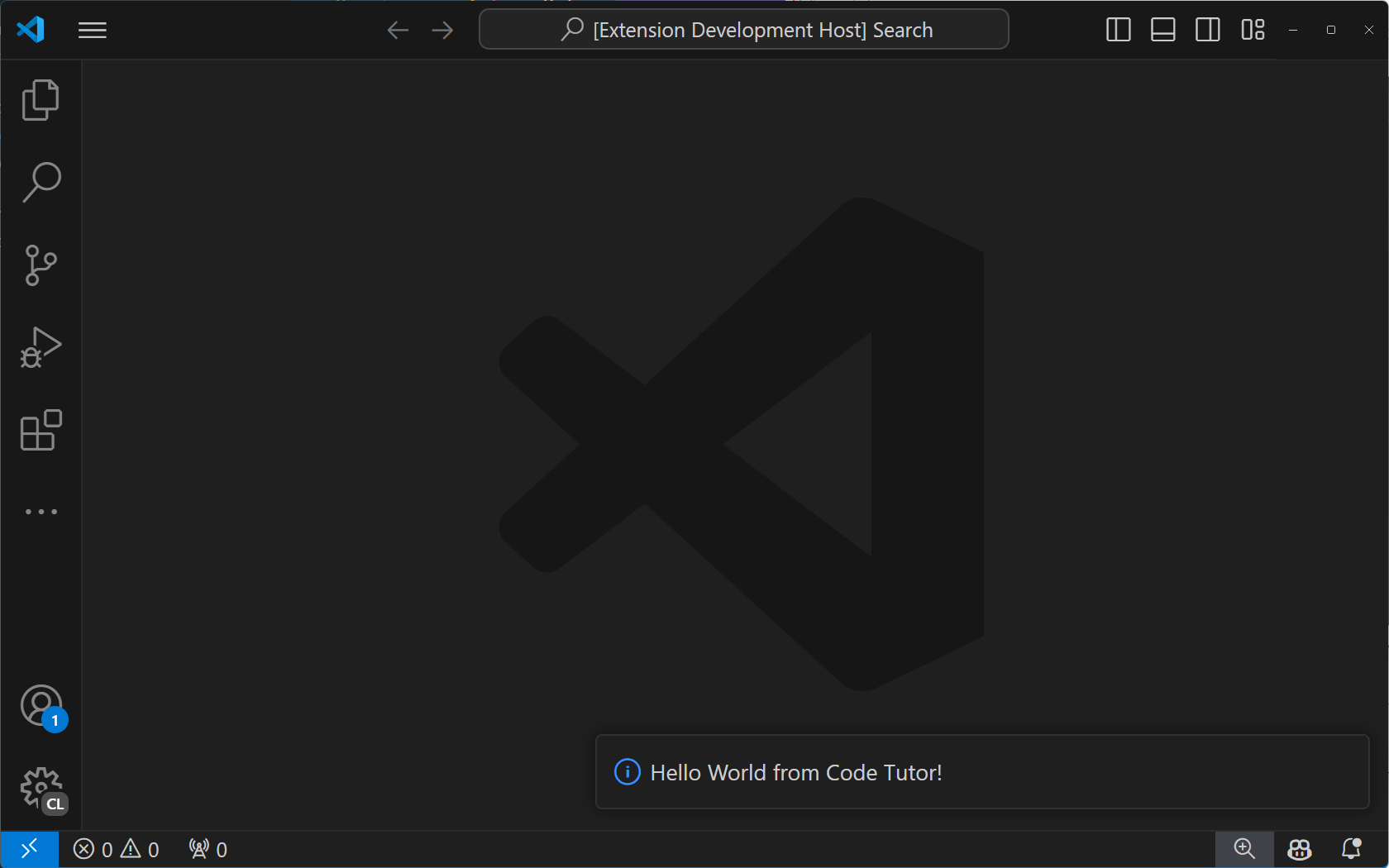
如果選擇 "Tutor Annotations" 命令,你將看到一個 "Hello World" 通知訊息。
實現 "annotate" 命令
為了讓我們的程式碼導師註釋生效,我們需要向它傳送一些程式碼並要求它提供註釋。我們將分三個步驟完成此操作
- 獲取當前使用者開啟的選項卡的程式碼,幷包含行號。
- 將該程式碼與自定義提示一起傳送到語言模型 API,該提示指示模型如何提供註釋。
- 解析註釋並在編輯器中顯示它們。
步驟 1:獲取帶行號的程式碼
要從當前選項卡獲取程式碼,我們需要對使用者開啟的選項卡進行引用。我們可以透過修改 registerCommand 方法為 registerTextEditorCommand 來實現。這兩個命令的區別在於,後者為我們提供了使用者開啟的選項卡的引用,稱為 TextEditor。
const disposable = vscode.commands.registerTextEditorCommand('code-tutor.annotate', async (textEditor: vscode.TextEditor) => {
現在我們可以使用 textEditor 引用來獲取 "可見編輯器空間" 中的所有程式碼。這是螢幕上可以看到的程式碼 - 它不包括在可見編輯器空間之上或之下的程式碼。
將以下方法新增到 extension.ts 檔案底部的 export function deactivate() { } 行的正上方。
function getVisibleCodeWithLineNumbers(textEditor: vscode.TextEditor) {
// get the position of the first and last visible lines
let currentLine = textEditor.visibleRanges[0].start.line;
const endLine = textEditor.visibleRanges[0].end.line;
let code = '';
// get the text from the line at the current position.
// The line number is 0-based, so we add 1 to it to make it 1-based.
while (currentLine < endLine) {
code += `${currentLine + 1}: ${textEditor.document.lineAt(currentLine).text} \n`;
// move to the next line position
currentLine++;
}
return code;
}
此程式碼使用 TextEditor 的 visibleRanges 屬性來獲取編輯器中當前可見行的位置。然後,它從第一行位置開始,移動到最後一行位置,將每一行程式碼連同行號一起新增到字串中。最後,它返回包含所有可見程式碼和行號的字串。
現在我們可以從 code-tutor.annotate 命令呼叫此方法。修改命令的實現,使其如下所示
const disposable = vscode.commands.registerTextEditorCommand(
'code-tutor.annotate',
async (textEditor: vscode.TextEditor) => {
// Get the code with line numbers from the current editor
const codeWithLineNumbers = getVisibleCodeWithLineNumbers(textEditor);
}
);
步驟 2:將程式碼和提示傳送到語言模型 API
下一步是呼叫 GitHub Copilot 語言模型,並將使用者的程式碼與建立註釋的指令一起傳送給它。
為此,我們首先需要指定要使用的聊天模型。我們在此選擇 4o,因為它對於我們正在構建的此類互動而言是一個快速且功能強大的模型。
const disposable = vscode.commands.registerTextEditorCommand(
'code-tutor.annotate',
async (textEditor: vscode.TextEditor) => {
// Get the code with line numbers from the current editor
const codeWithLineNumbers = getVisibleCodeWithLineNumbers(textEditor);
// select the 4o chat model
let [model] = await vscode.lm.selectChatModels({
vendor: 'copilot',
family: 'gpt-4o'
});
}
);
我們需要指示 - 或 "提示" - 來告訴模型建立註釋以及我們希望響應的格式。將以下程式碼新增到檔案頂部,緊跟在 import 之後。
const ANNOTATION_PROMPT = `You are a code tutor who helps students learn how to write better code. Your job is to evaluate a block of code that the user gives you and then annotate any lines that could be improved with a brief suggestion and the reason why you are making that suggestion. Only make suggestions when you feel the severity is enough that it will impact the readability and maintainability of the code. Be friendly with your suggestions and remember that these are students so they need gentle guidance. Format each suggestion as a single JSON object. It is not necessary to wrap your response in triple backticks. Here is an example of what your response should look like:
{ "line": 1, "suggestion": "I think you should use a for loop instead of a while loop. A for loop is more concise and easier to read." }{ "line": 12, "suggestion": "I think you should use a for loop instead of a while loop. A for loop is more concise and easier to read." }
`;
這是一個特殊的提示,它指示語言模型如何生成註釋。它還包括模型應如何格式化其響應的示例。這些示例(也稱為 "multi-shot")使我們能夠定義響應的格式,以便我們解析並將其顯示為註釋。
我們將訊息以陣列形式傳遞給模型。此陣列可以包含任意數量的訊息。在我們的例子中,它包含提示,然後是帶行號的使用者程式碼。
const disposable = vscode.commands.registerTextEditorCommand(
'code-tutor.annotate',
async (textEditor: vscode.TextEditor) => {
// Get the code with line numbers from the current editor
const codeWithLineNumbers = getVisibleCodeWithLineNumbers(textEditor);
// select the 4o chat model
let [model] = await vscode.lm.selectChatModels({
vendor: 'copilot',
family: 'gpt-4o'
});
// init the chat message
const messages = [
vscode.LanguageModelChatMessage.User(ANNOTATION_PROMPT),
vscode.LanguageModelChatMessage.User(codeWithLineNumbers)
];
}
);
要將訊息傳送到模型,我們首先需要確保所選模型可用。這會處理擴充套件未準備好或使用者未登入 GitHub Copilot 的情況。然後,我們將訊息傳送到模型。
const disposable = vscode.commands.registerTextEditorCommand(
'code-tutor.annotate',
async (textEditor: vscode.TextEditor) => {
// Get the code with line numbers from the current editor
const codeWithLineNumbers = getVisibleCodeWithLineNumbers(textEditor);
// select the 4o chat model
let [model] = await vscode.lm.selectChatModels({
vendor: 'copilot',
family: 'gpt-4o'
});
// init the chat message
const messages = [
vscode.LanguageModelChatMessage.User(ANNOTATION_PROMPT),
vscode.LanguageModelChatMessage.User(codeWithLineNumbers)
];
// make sure the model is available
if (model) {
// send the messages array to the model and get the response
let chatResponse = await model.sendRequest(
messages,
{},
new vscode.CancellationTokenSource().token
);
// handle chat response
await parseChatResponse(chatResponse, textEditor);
}
}
);
聊天響應以片段形式返回。這些片段通常包含單個單詞,但有時僅包含標點符號。為了在響應流式傳輸時顯示註釋,我們希望等到獲得完整的註釋後再顯示它。由於我們指示模型返回其響應的方式,我們知道當看到結束的 } 時,我們就獲得了一個完整的註釋。然後,我們可以解析註釋並在編輯器中顯示它。
在 extension.ts 檔案中的 getVisibleCodeWithLineNumbers 方法正上方新增缺失的 parseChatResponse 函式。
async function parseChatResponse(
chatResponse: vscode.LanguageModelChatResponse,
textEditor: vscode.TextEditor
) {
let accumulatedResponse = '';
for await (const fragment of chatResponse.text) {
accumulatedResponse += fragment;
// if the fragment is a }, we can try to parse the whole line
if (fragment.includes('}')) {
try {
const annotation = JSON.parse(accumulatedResponse);
applyDecoration(textEditor, annotation.line, annotation.suggestion);
// reset the accumulator for the next line
accumulatedResponse = '';
} catch (e) {
// do nothing
}
}
}
}
我們需要最後一個方法來實際顯示註釋。VS Code 將這些稱為 "裝飾"。在 extension.ts 檔案中的 parseChatResponse 方法正上方新增以下方法。
function applyDecoration(editor: vscode.TextEditor, line: number, suggestion: string) {
const decorationType = vscode.window.createTextEditorDecorationType({
after: {
contentText: ` ${suggestion.substring(0, 25) + '...'}`,
color: 'grey'
}
});
// get the end of the line with the specified line number
const lineLength = editor.document.lineAt(line - 1).text.length;
const range = new vscode.Range(
new vscode.Position(line - 1, lineLength),
new vscode.Position(line - 1, lineLength)
);
const decoration = { range: range, hoverMessage: suggestion };
vscode.window.activeTextEditor?.setDecorations(decorationType, [decoration]);
}
此方法接收我們從模型解析的註釋,並使用它來建立裝飾。這是透過首先建立一個 TextEditorDecorationType 來完成的,該型別指定了裝飾的外觀。在這種情況下,我們只新增一個灰色的註釋,並將其截斷為 25 個字元。當用戶將滑鼠懸停在訊息上時,我們將顯示完整的訊息。
然後,我們設定裝飾應顯示的位置。我們需要它出現在註釋中指定的行號上,並在行末。
最後,我們將裝飾設定在活動文字編輯器上,這就是導致註釋出現在編輯器中的原因。
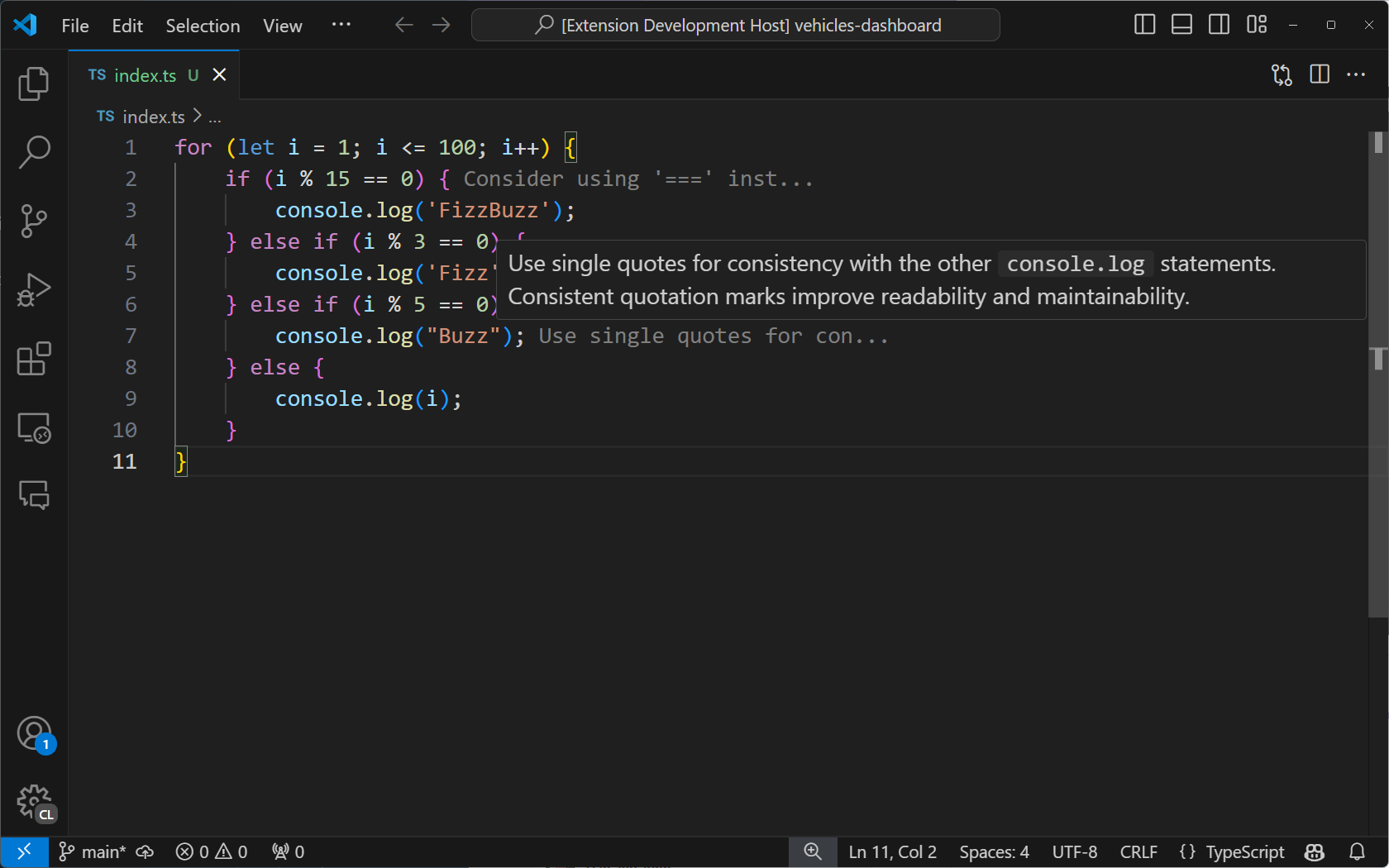
如果你的擴充套件仍在執行,請透過選擇除錯欄中的綠色箭頭來重新啟動它。如果關閉了除錯會話,請按 F5 執行擴充套件。在開啟的新 VS Code 視窗例項中開啟一個程式碼檔案。從命令面板中選擇 "Toggle Tutor Annotations" 後,你應該會看到程式碼註釋出現在編輯器中。
向編輯器標題欄新增一個按鈕
你可以使你的命令從命令面板以外的地方呼叫。在我們的例子中,我們可以在當前選項卡的頂部新增一個按鈕,讓使用者輕鬆切換註釋。
為此,請按以下方式修改 package.json 的 "contributes" 部分
"contributes": {
"commands": [
{
"command": "code-tutor.annotate",
"title": "Toggle Tutor Annotations",
"icon": "$(comment)"
}
],
"menus": {
"editor/title": [
{
"command": "code-tutor.annotate",
"group": "navigation"
}
]
}
}
這會在編輯器標題欄的導航區域(右側)顯示一個按鈕。"icon" 來自 產品圖示參考。
使用綠色箭頭重新啟動你的擴充套件,如果擴充套件尚未執行,請按 F5。現在你應該會看到一個評論圖示,它將觸發 "Toggle Tutor Annotations" 命令。

後續步驟
在本教程中,你學習瞭如何建立一個將 AI 整合到編輯器的 VS Code 擴充套件,並使用了語言模型 API。你使用了 VS Code 擴充套件 API 來獲取當前選項卡中的程式碼,將其與自定義提示一起傳送給模型,然後使用裝飾器在編輯器中解析並顯示模型結果。
接下來,你可以擴充套件你的程式碼導師擴充套件,以 包含一個聊天參與者,這將允許使用者透過 GitHub Copilot 聊天介面直接與你的擴充套件進行互動。你還可以 探索 VS Code 中的完整 API,以探索構建自定義 AI 體驗的新方法。
你可以在 vscode-extensions-sample 儲存庫中找到本教程的完整原始碼。